Learning module:
Law and democracy Defining Moments
The Australian court hierarchy
1.1 What is the role of the High Court?

Australia has a court hierarchy. It includes state, territory and federal courts. The state and territory courts deal with matters under state and territory laws. The federal courts deal with matters involving federal law, and with appeals from state and territory courts.
Here is a diagram showing the position of the High Court in the Australian court hierarchy:
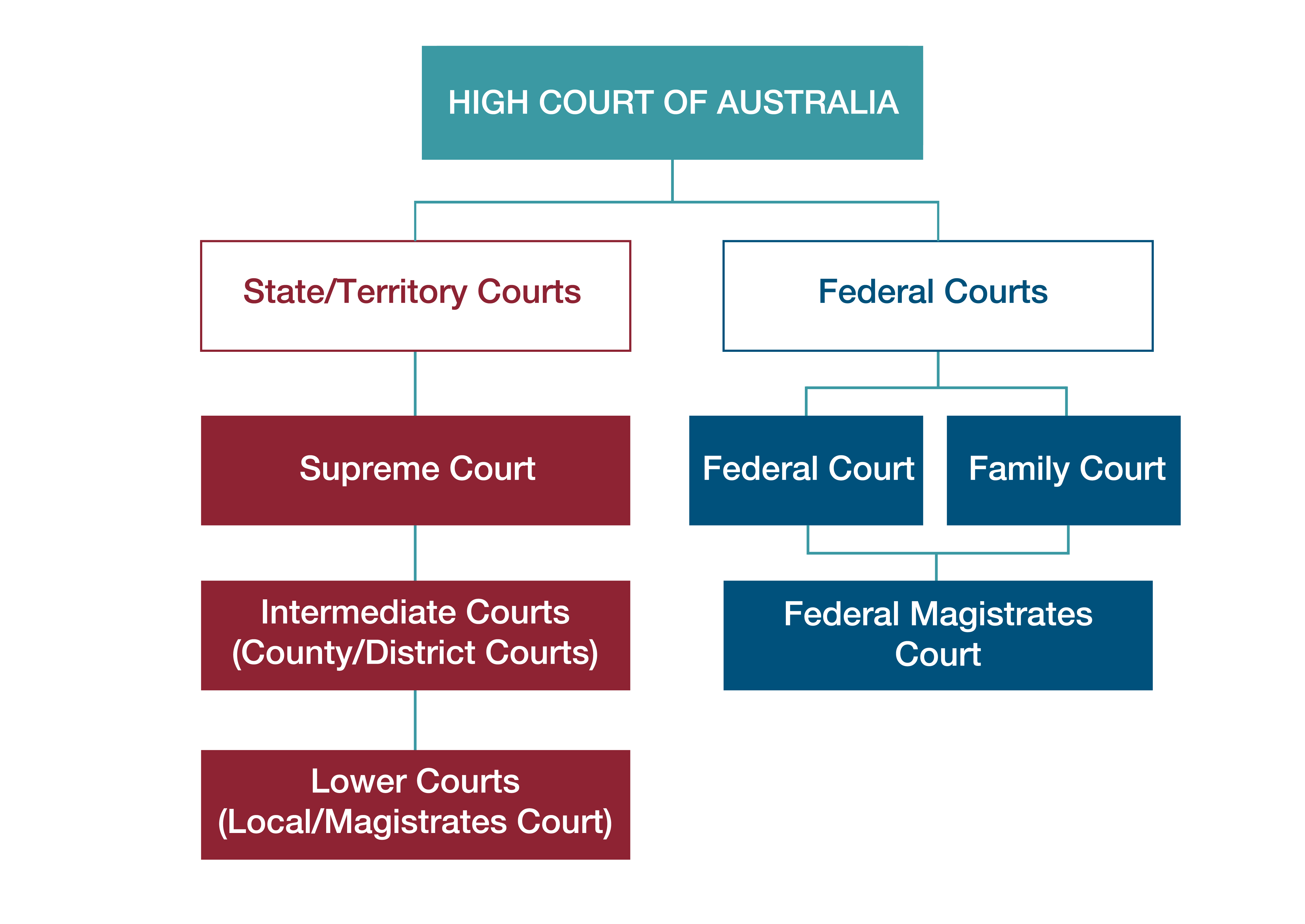
The High Court has two main roles:
- It is the highest court of appeal in Australia.
- It has the task of interpreting the Australian Constitution when there is any uncertainty or ambiguity about its meaning.
The functions of the High Court are to:
- interpret and apply the law of Australia
- decide cases of special federal significance including challenges to the constitutional validity of laws
- hear appeals, by special leave, from federal, state and territory courts.
1. Describe the role of the High Court in the Australian court system.
2. In your investigation of the role of the High Court you will be exploring two very important defining moments in Australian history: the Franklin Dam case of the 1980s and the Mabo case of the 1990s.From what you might already know of these cases, which of the High Court’s main functions do you think you will be examining?
In fact you are about to explore how the High Court works in both its appeals function and its role in interpreting the Australian Constitution. You will also see how the Australian Parliament’s powers in foreign policy matters affect what happens within Australia.
You can do this through these important case studies:
|
‘Stretching’ the Constitution: The Franklin Dam The High Court expands federal powers over the environment. |
Courts making law: The Mabo case The High Court makes law about Indigenous land rights. |







