Petroglyphs and pictographs
About 30,000 years ago: Earliest known Australian rock art
Petroglyphs and pictographs
About 30,000 years ago: Earliest known Australian rock art
In a snapshot
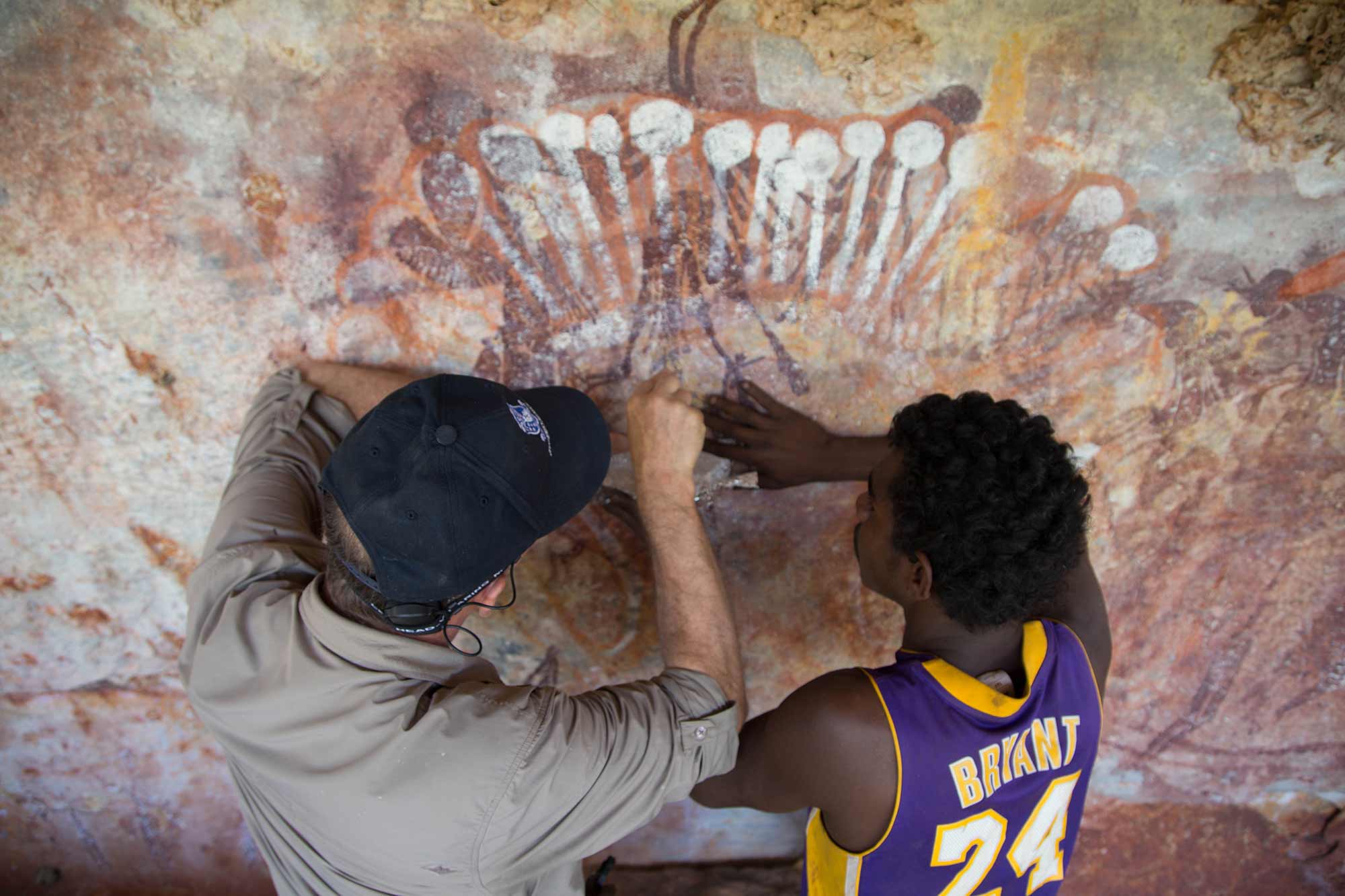
Rock art is an extremely important part of First Nations cultures in Australia. There are more than 100,000 rock art sites in Australia. First Nations peoples consider many rock art locations to be sacred sites. Viewing and studying rock art helps us understand how people lived in Australia since they arrived between 65,000 and 80,000 years ago.

 Can you find out?
Can you find out?
1. What are the major types of Australian rock art? How are they different?
2. What is the main purpose of rock art?
3. Why is rock art important to First Nations peoples?
What is rock art?
Rock art is the oldest human art form that survives today. The first humans arrived in Australia between 65,000 and 80,000 years ago. Australian rock art has been dated to around 30,000 years ago. But there might be much older rock art sites on the continent. For First Nations peoples in Australia, rock art sites are records of their ongoing history since time immemorial.
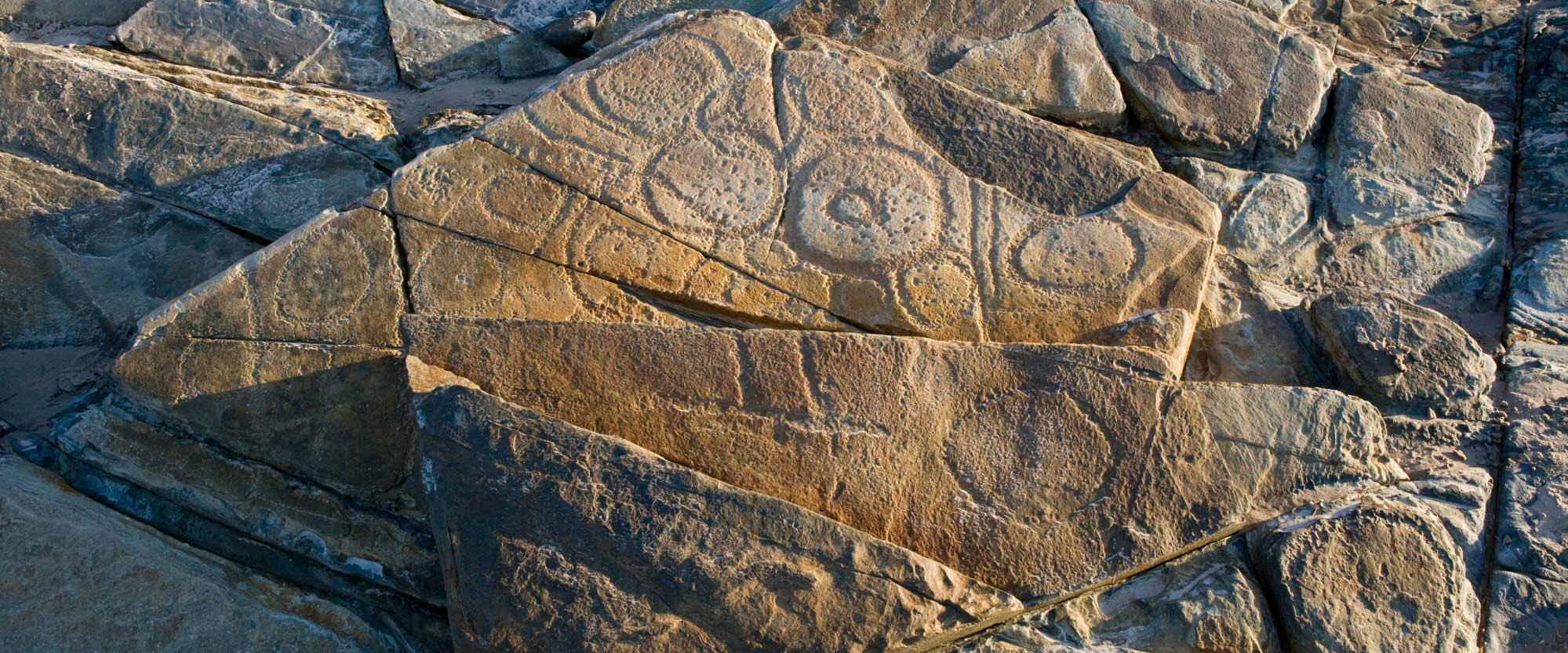
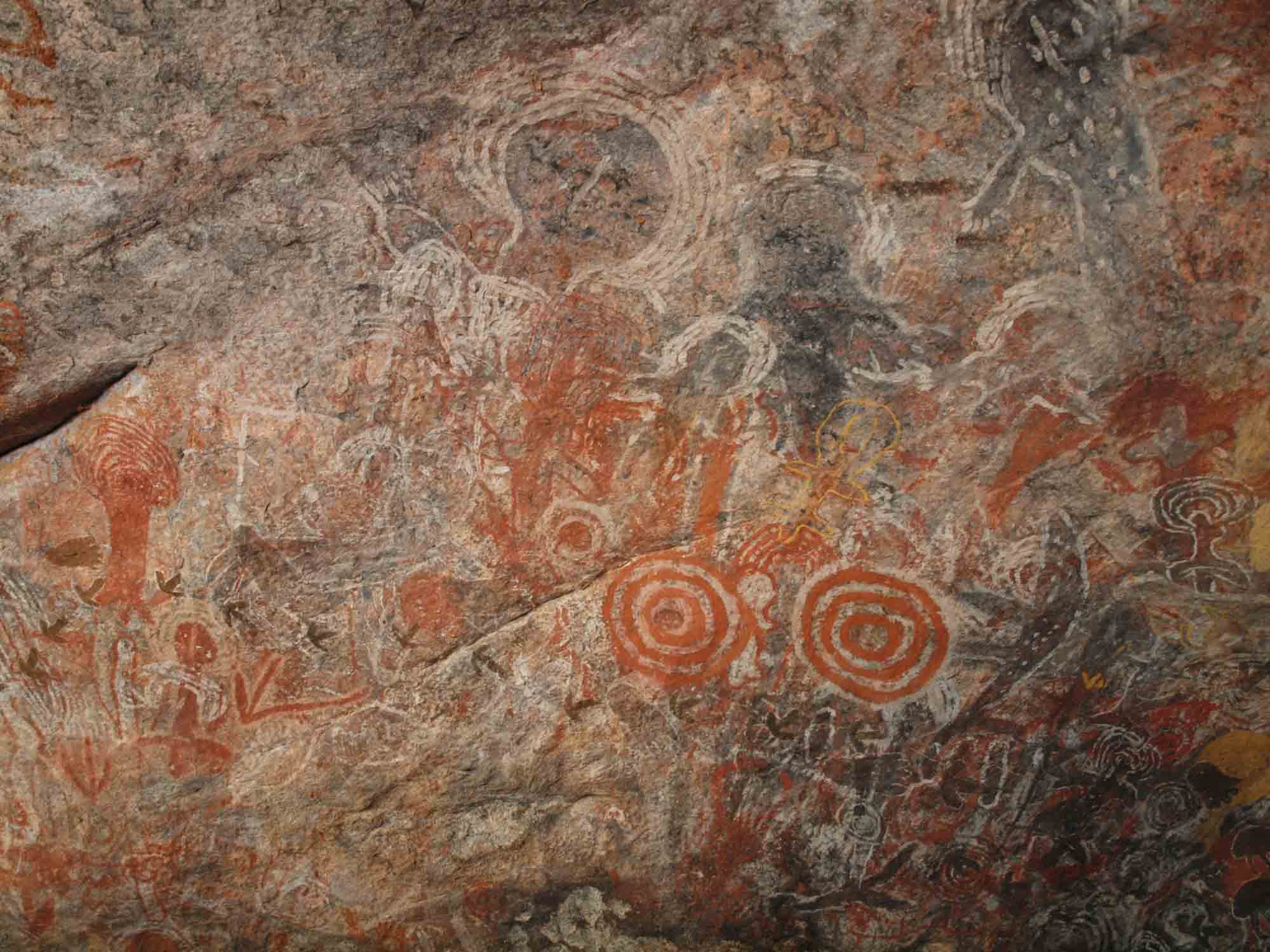
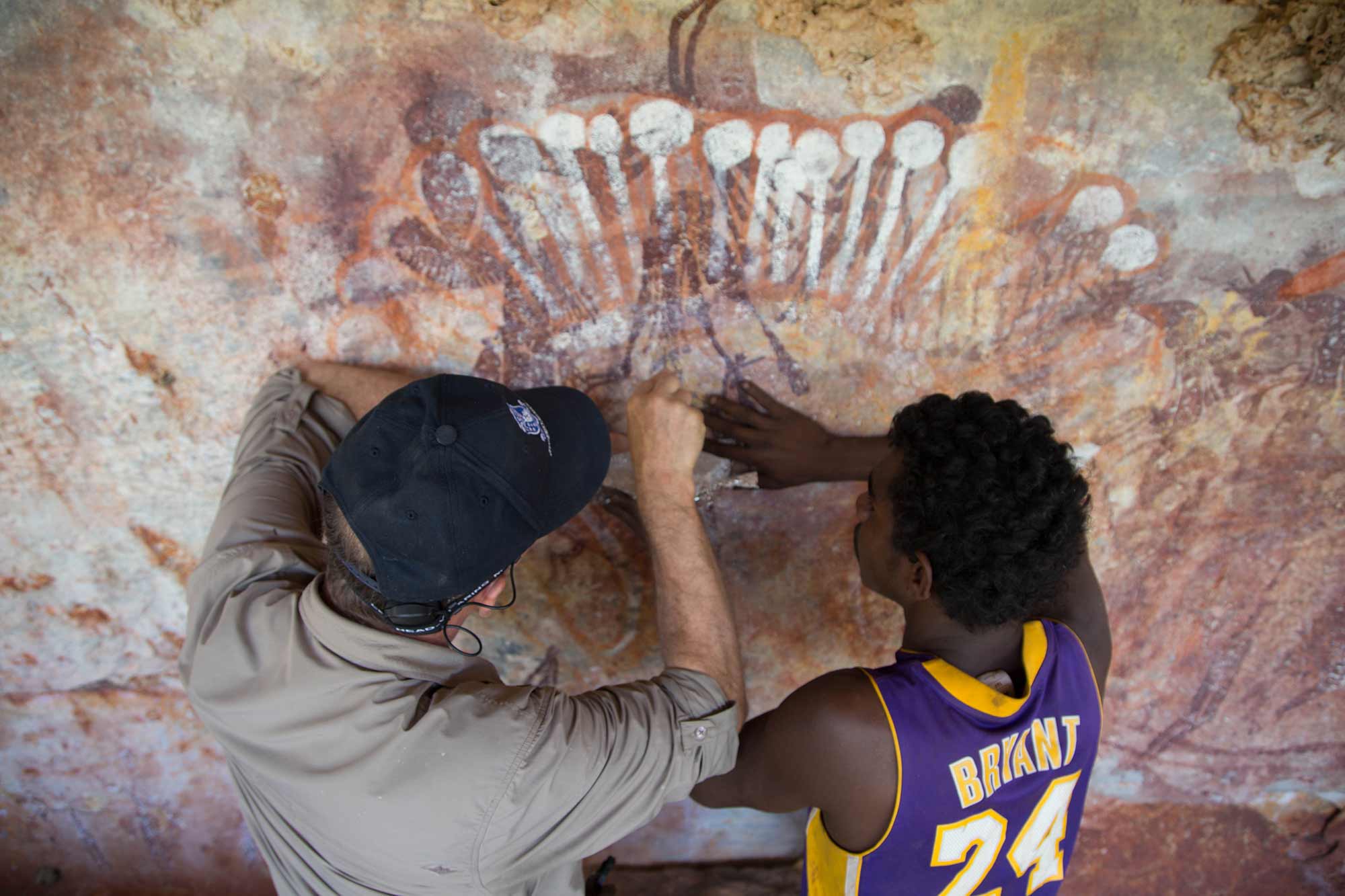
First Nations peoples created and continue to create different kinds of rock art. Petroglyph and pictograph rock art are the two main forms.
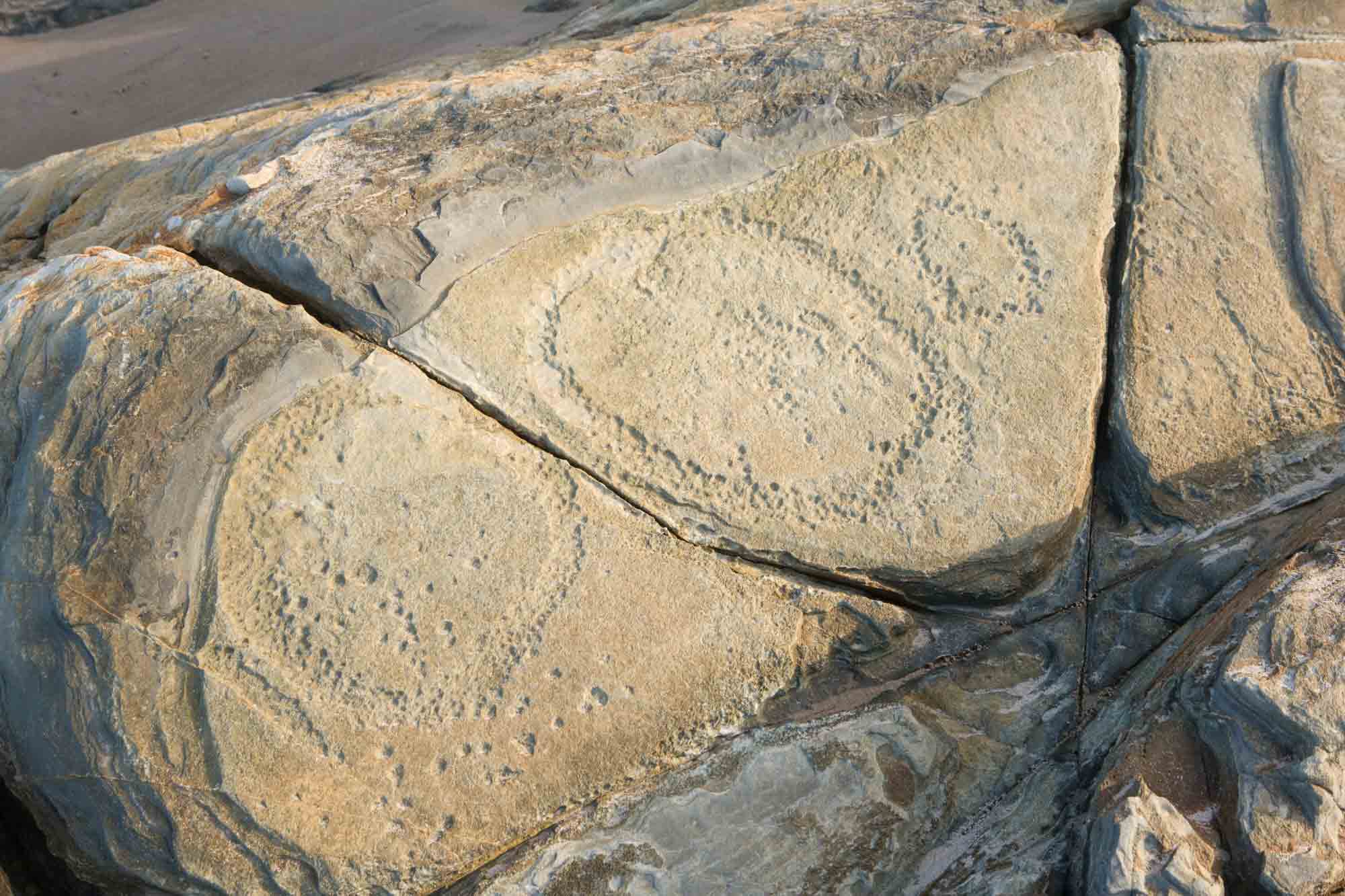
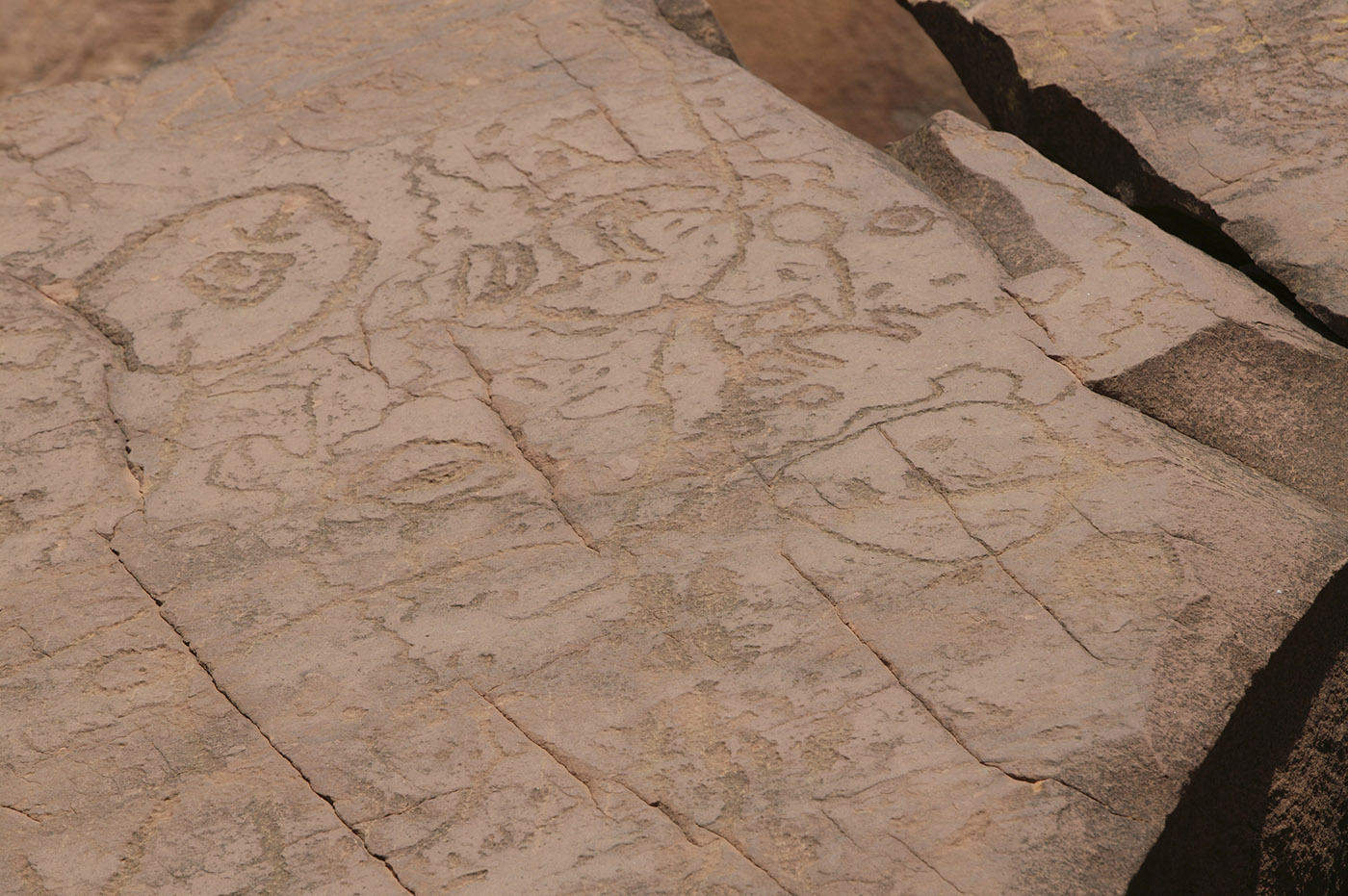
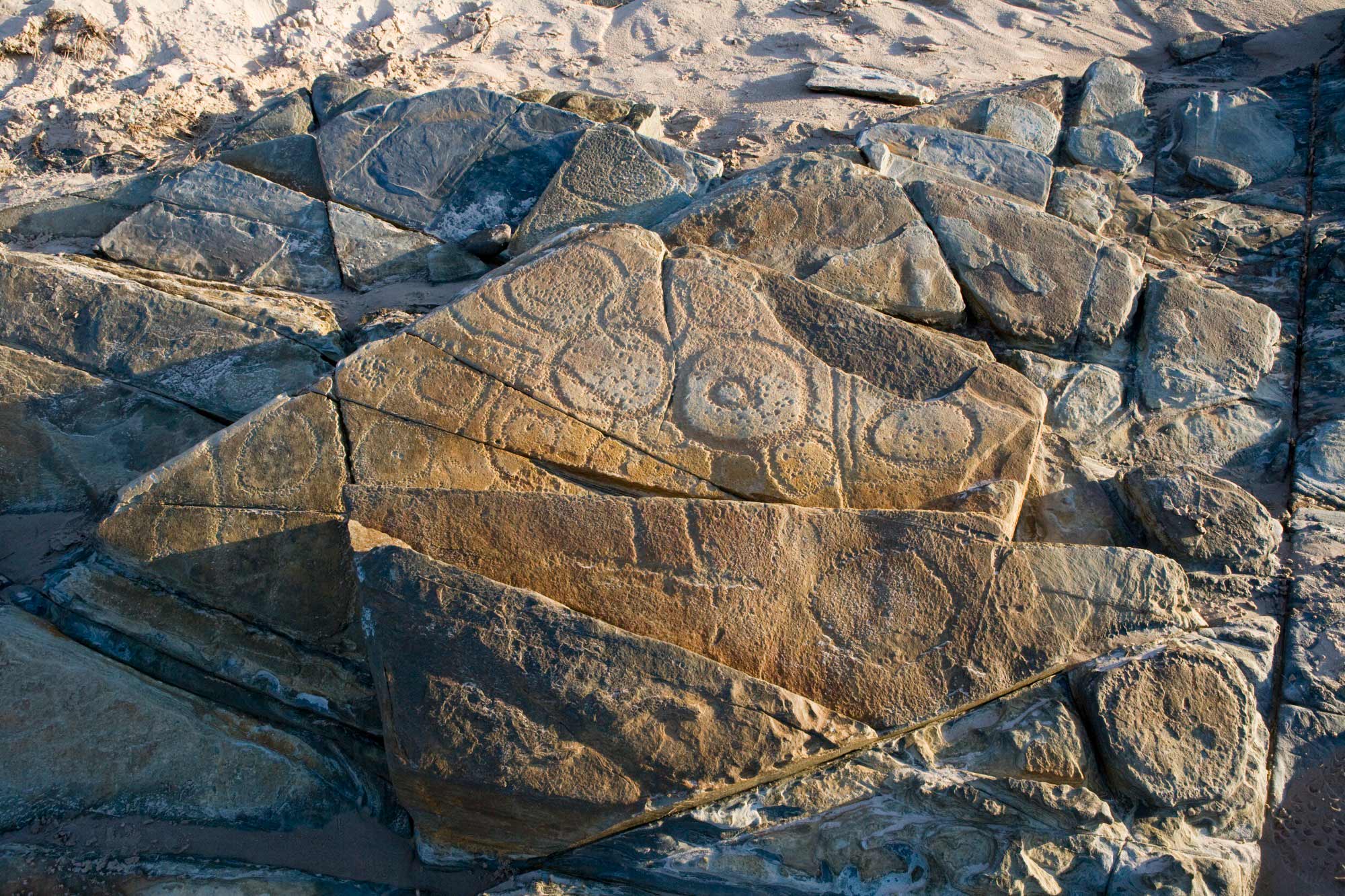
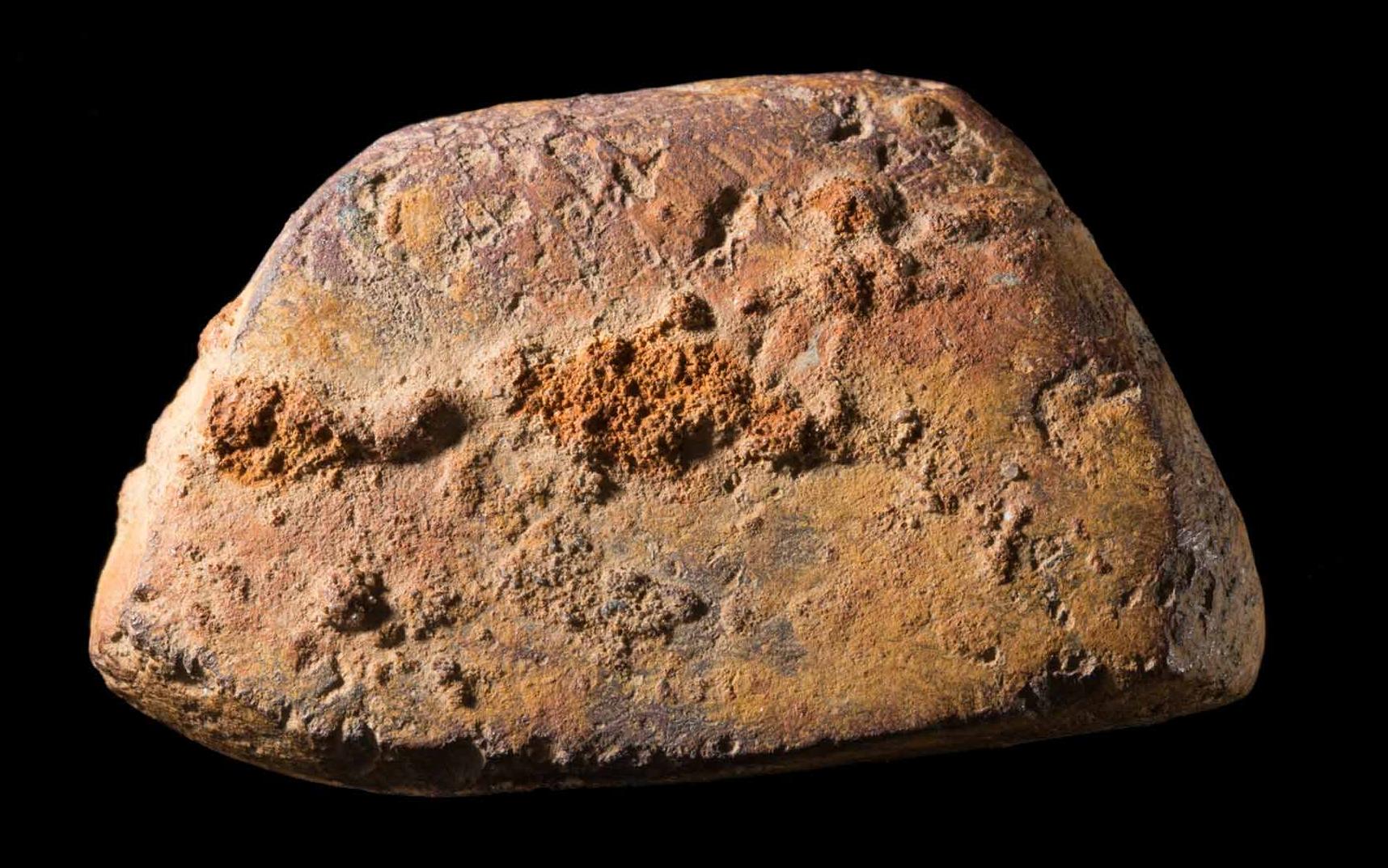
To create a petroglyph, people engrave rock by pecking, hammering or chipping away at a surface to make an image. These images have shapes like circles, arcs, dots or animal tracks.
To create a pictograph, people paint minerals like charcoal, clay, chalk and ochre on a rock surface. People can use dry or wet colours to create pictographs, by using their fingers or brushes (made from chewed sticks or hair) to paint with. In pictographs, you see images you can recognise more easily, like humans or animals. Petroglyphs can be found around Australia, but pictographs survive only in sheltered areas like caves.
Rock art can be simple or very complex. The type of artwork used depends on the individual artist and their cultural group.
‘Our story is in the land. It is written in those sacred places.’
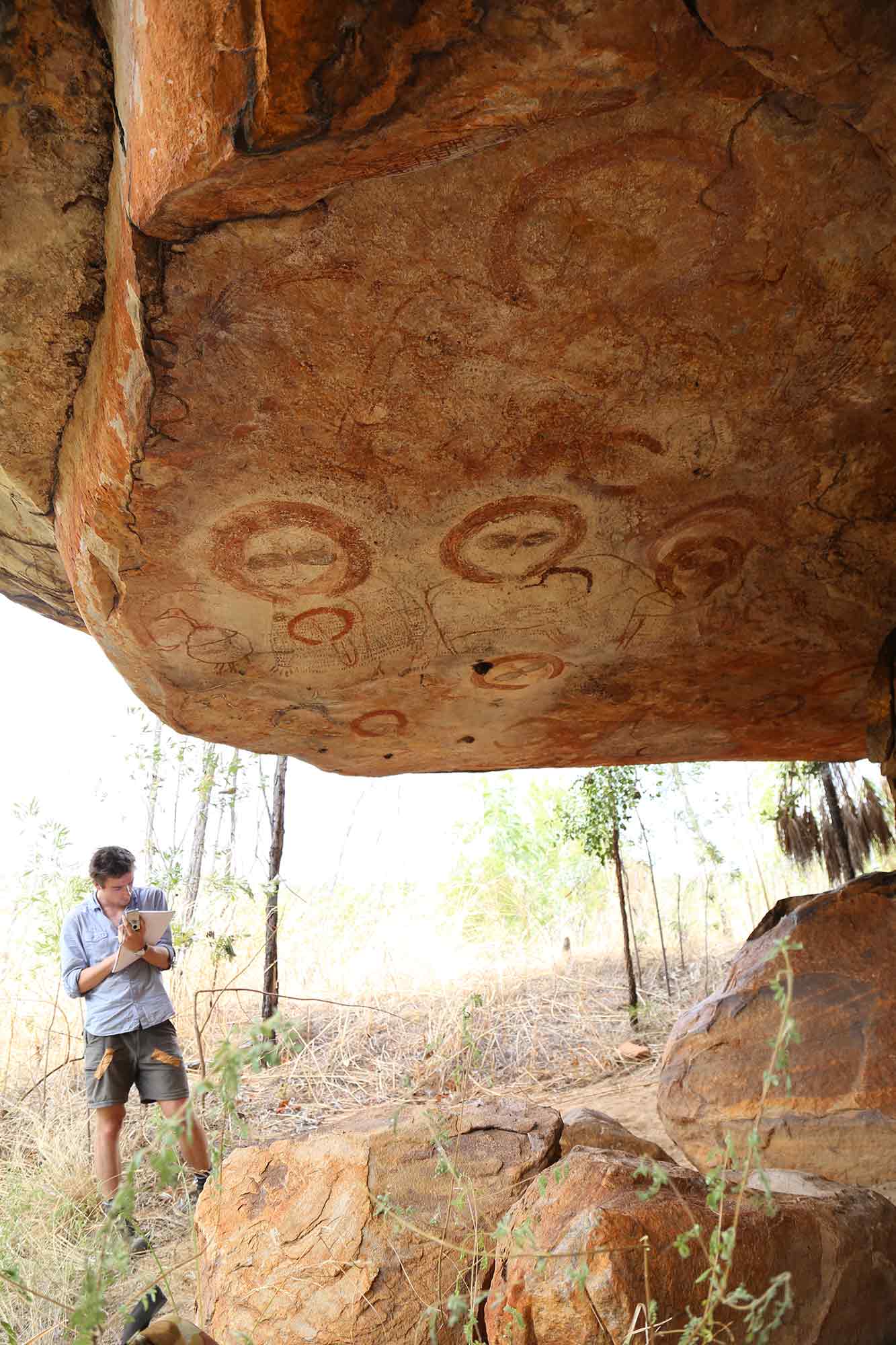

Why is rock art important?
All cultures on earth use pictures to tell stories. From the time they arrived in Australia, First Nations peoples used artworks in sacred and public places to record their stories.
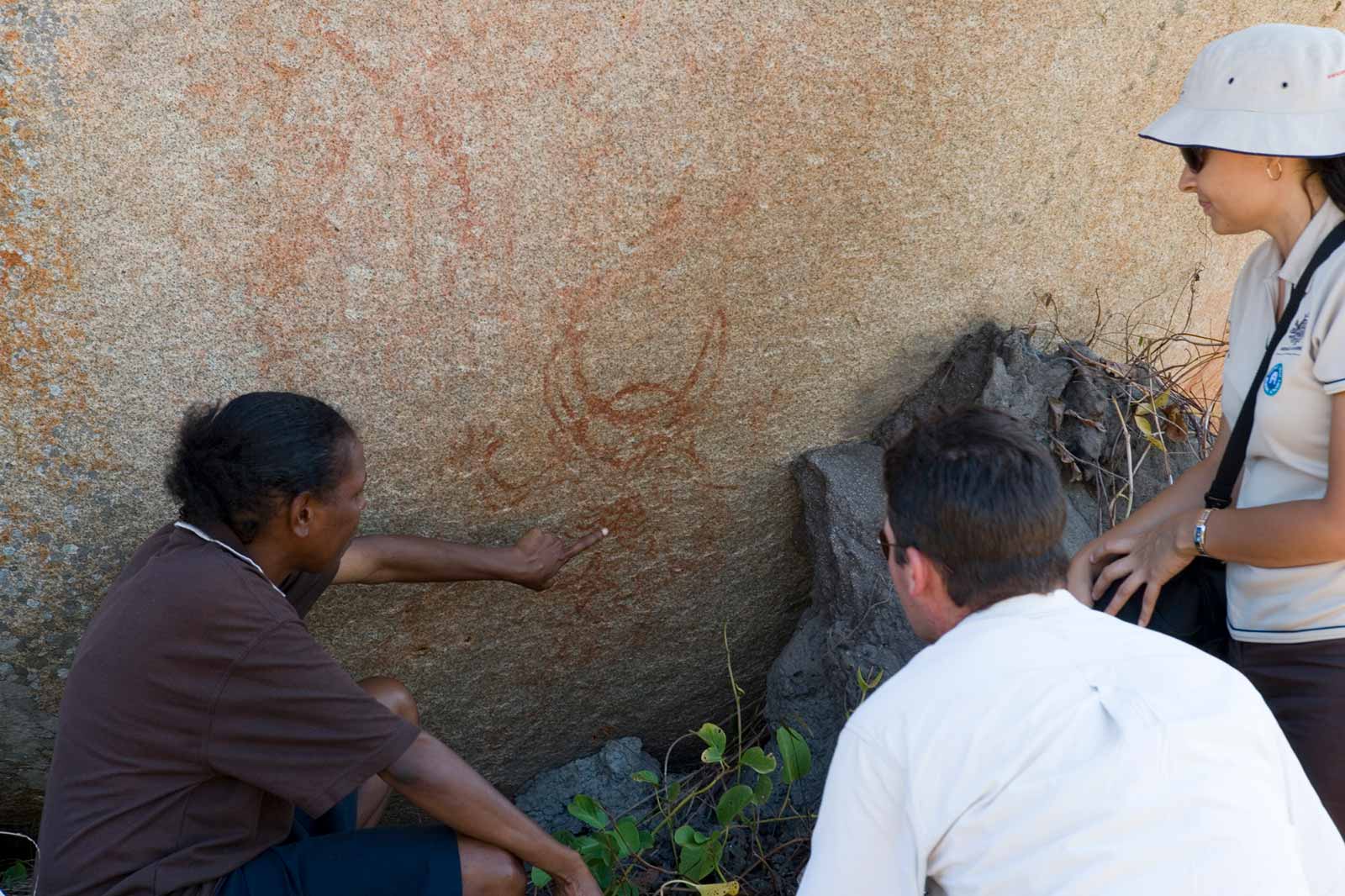
First Nations peoples continue to pass down knowledge about rock art today. This tradition has continued for thousands of years, sometimes directly from the original artists themselves. First Nations peoples consider many rock art locations to be sacred sites.
Rock art is therefore an extremely valuable historic, artistic and spiritual resource.
How is rock art used for learning on Country?
How are rock art engravings (petroglyphs), stencils and prints made? Visit a rock art site in the Blue Mountains with First Nations archaeologist Wayne Brennan, in the Hey History! podcast.
What will happen to Australia’s rock art?
Rock art is an important part of First Nations life and culture, and needs to be protected.
In 2025 there are seven rock art on Australia’s National Heritage List. These are the Dampier Archipelago (including Burrup Peninsula), Grampians National Park, Kakadu National Park, Koonalda Cave, Uluru-Kata Tjuta National Park, the Tasmanian Wilderness and the West Kimberley. All of these sites are protected under Australian laws. In urban areas rock art sites are vulnerable to development and vandalism, while sites in remote locations can be threatened by mining, industrial and pastoral activities, as well as natural disasters.
If we protect and care for rock art, all Australians can appreciate it for generations to come.
Read a longer version of this Defining Moment on the National Museum of Australia’s website.
Research task
On a map of Australia, mark the seven rock art sites on Australia’s National Heritage List. What does the location of these sites tell you about Australia before Europeans arrived?
Department of Agriculture, Water and the Environment
 What did you learn?
What did you learn?
1. What are the major types of Australian rock art? How are they different?
2. What is the main purpose of rock art?
3. Why is rock art important to First Nations peoples?