A humiliating disaster
1942: Japanese Imperial Army invades Singapore
A humiliating disaster
1942: Japanese Imperial Army invades Singapore
In a snapshot
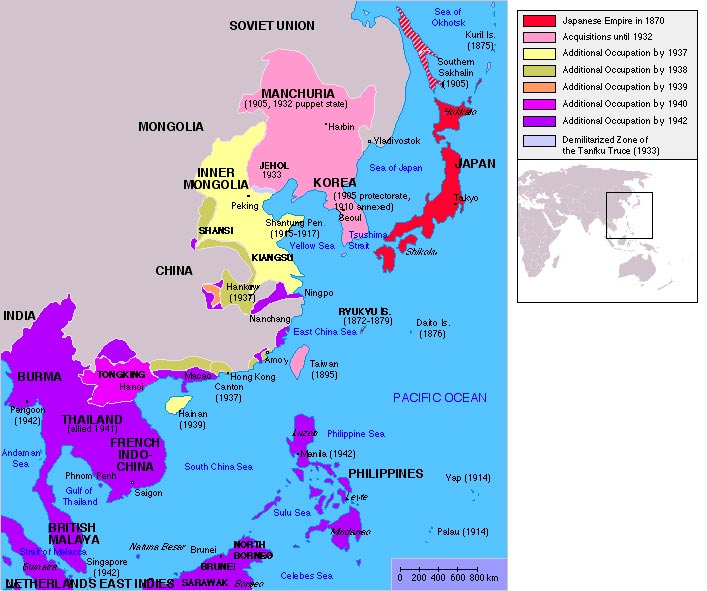
In 1942 the Japanese Imperial Army invaded Singapore, an island under British control. This was a humiliating disaster for the British Empire in the Pacific. Britain’s Singapore Strategy, supported by Australia, had been to build a naval base on the island to defend the region from a Japanese invasion. The Strategy had failed. After the Second World War, Australia’s traditional reliance on Britain for military protection shifted to the United States, which became the dominant power in the Pacific.

 Can you find out?
Can you find out?
1. Why did Australia and New Zealand build a naval base in Singapore?
2. How successful was the Japanese invasion of the Malay Peninsula? What contributed to this success?
3. What events led Australia to rely on the United States for its defence after the fall of Singapore?
What was the Singapore Strategy?
After the First World War (1914–18) Australia considered Japan its biggest threat because it was expanding its empire across the Pacific Ocean. Australia and New Zealand built a massive 54-square-kilometre naval base in Singapore. The base could hold a large British fleet that could defend Australia and New Zealand from a Japanese invasion. In the 1920s the Australian Government led by Prime Minister Stanley Bruce believed that this naval base — the core of the Singapore Strategy — would be cheaper than other defence plans.
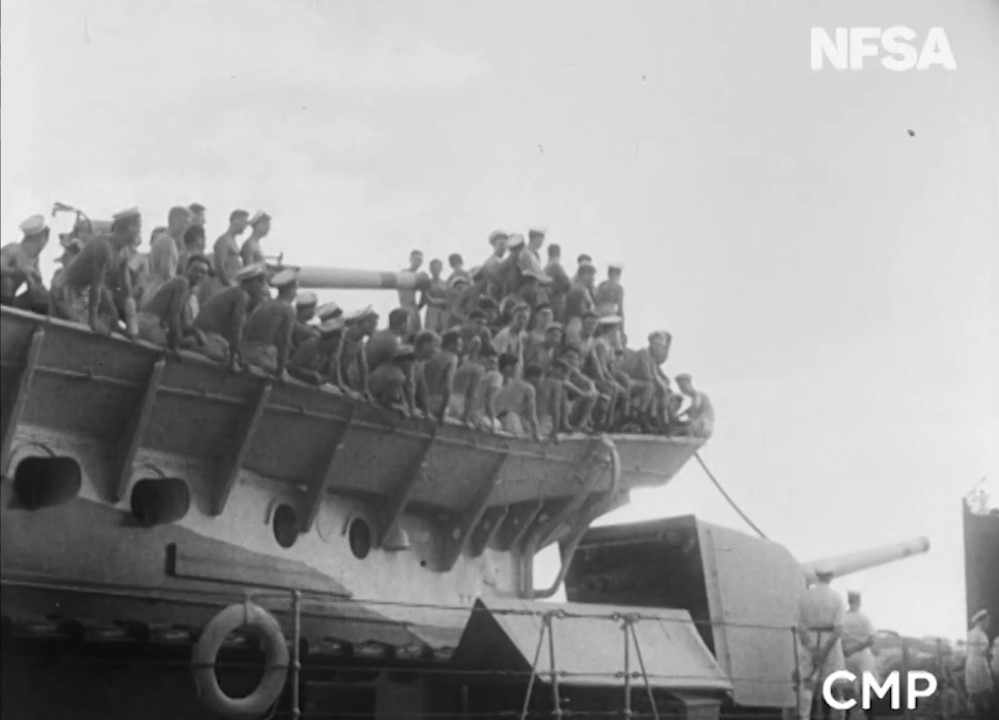
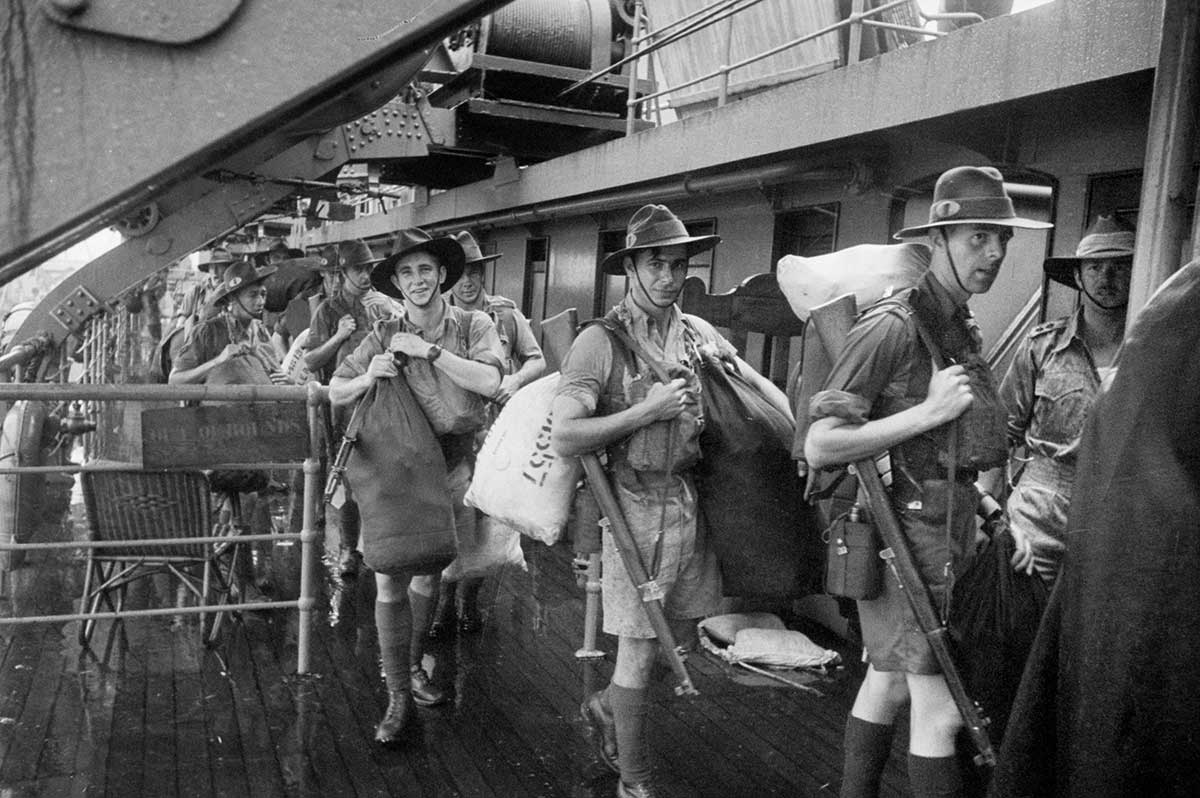
When the Second World War broke out in 1939, Australia sent its troops to help Britain fight Nazi Germany and its allies in Europe and North Africa. Britain focused on defending itself and the campaign in North Africa, rather than fighting Japan in the Pacific. It sent only two battleships to try to stop the invading Japanese Army.
‘Without any inhibitions of any kind, I make it clear that Australia looks to America, free of any pangs as to our traditional links or kinship with the United Kingdom.’

Why did the Singapore Strategy fail?
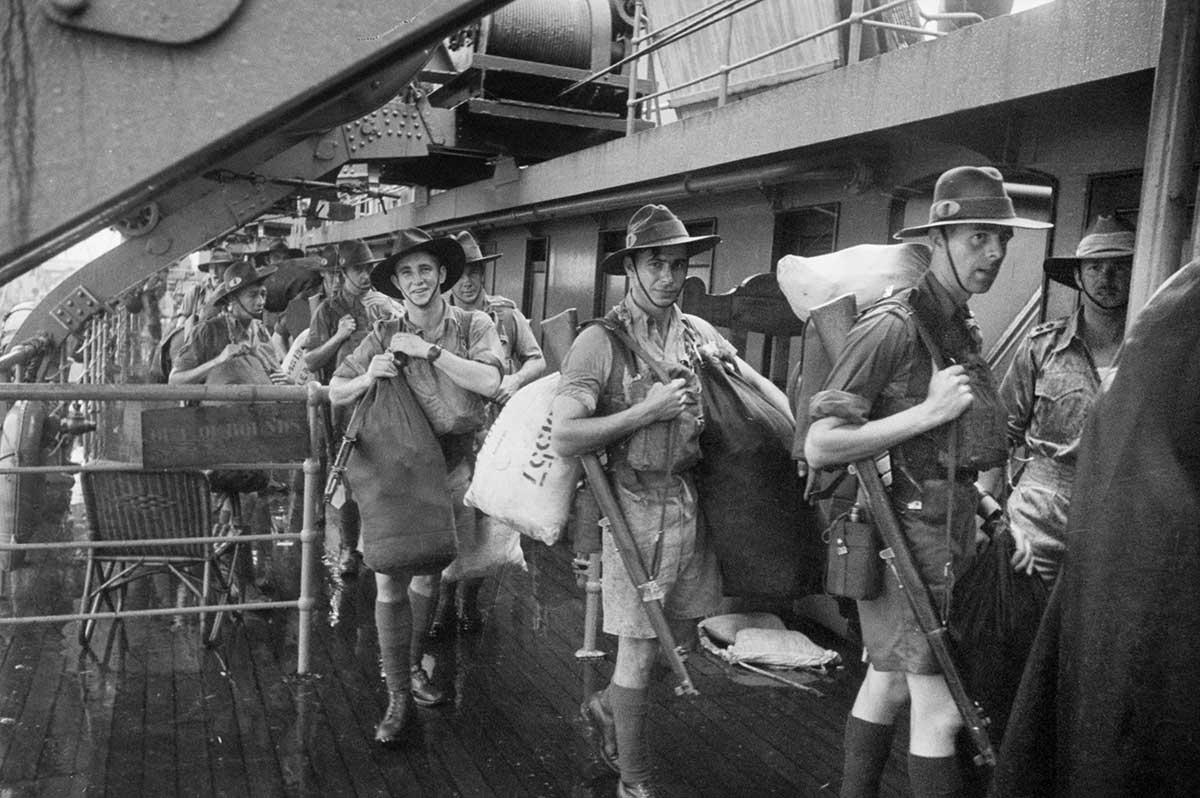
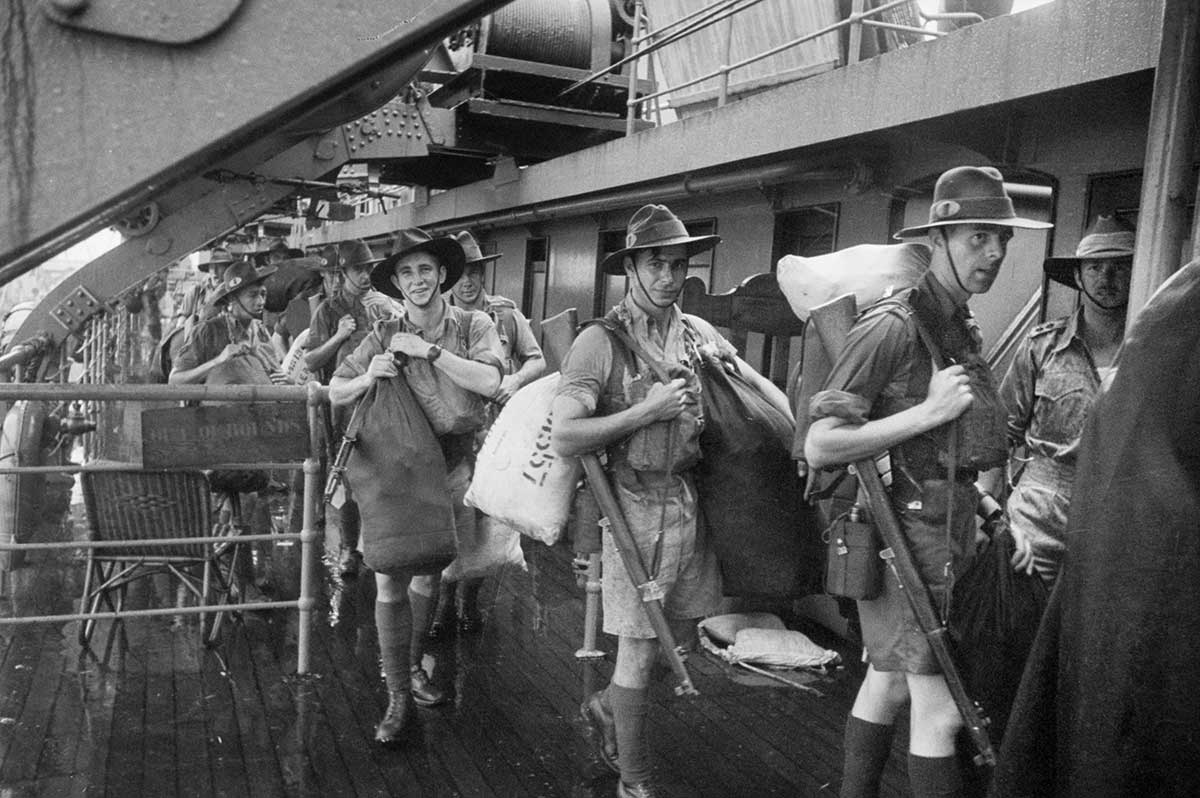
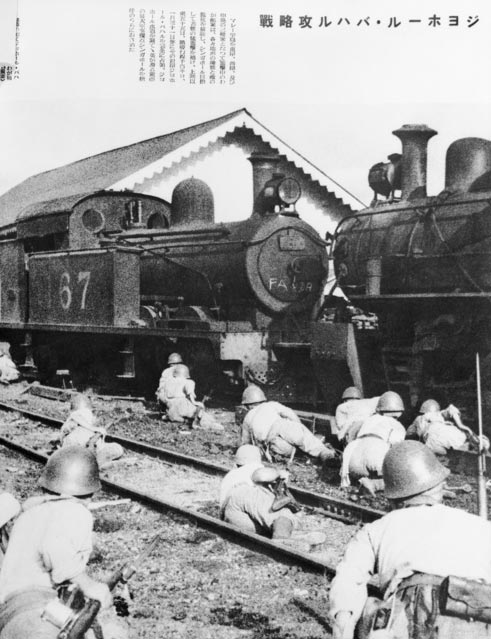
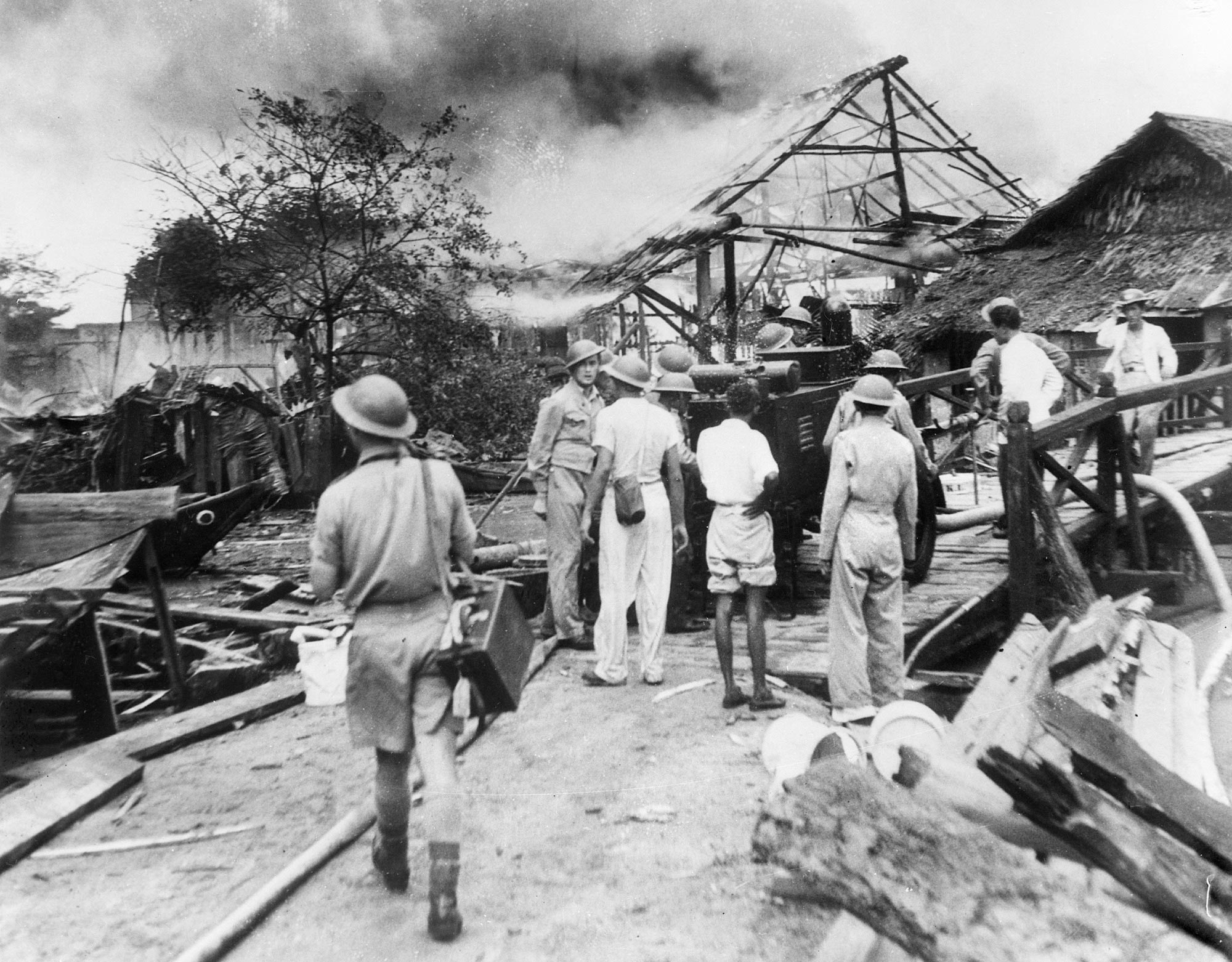
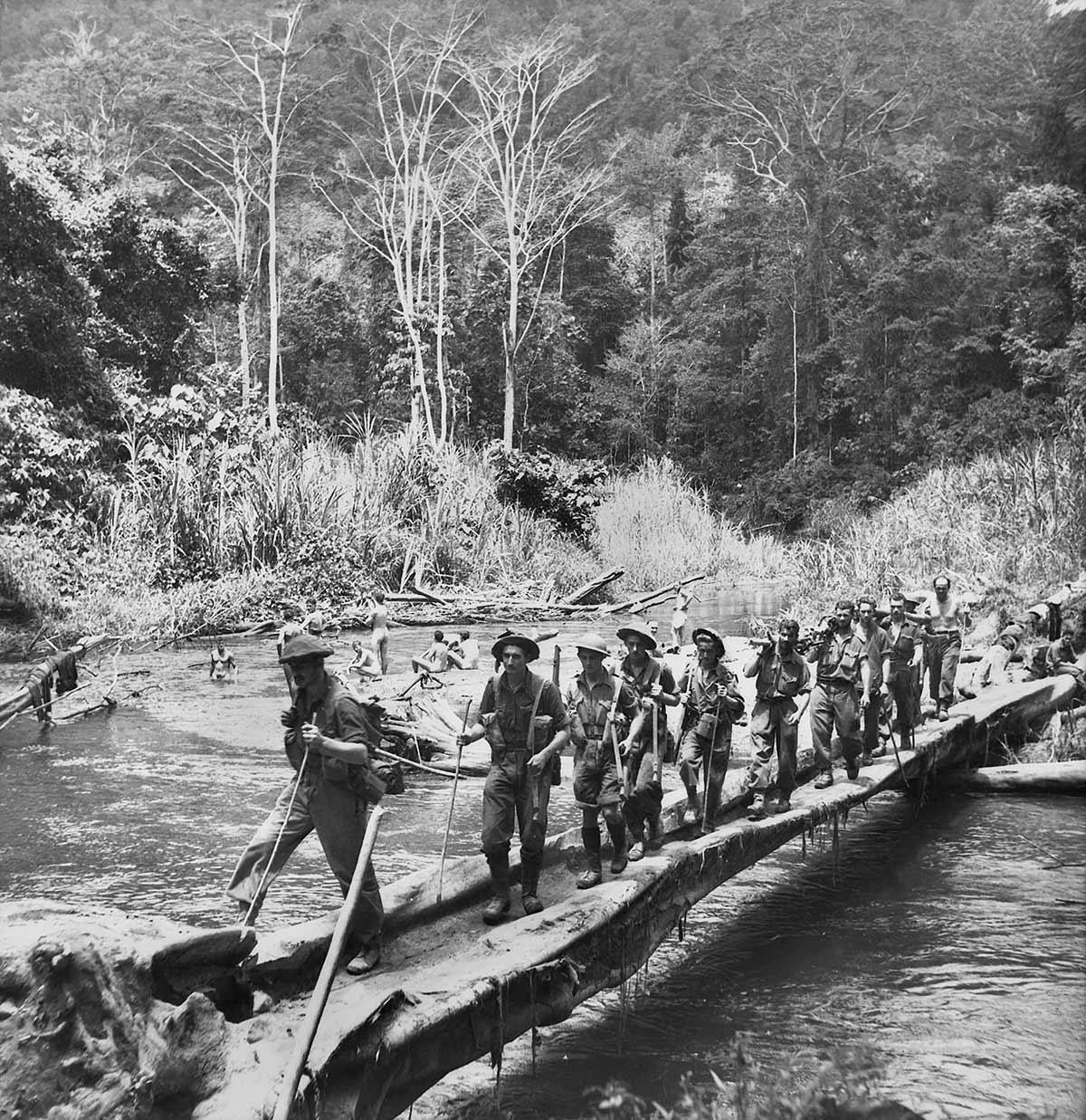
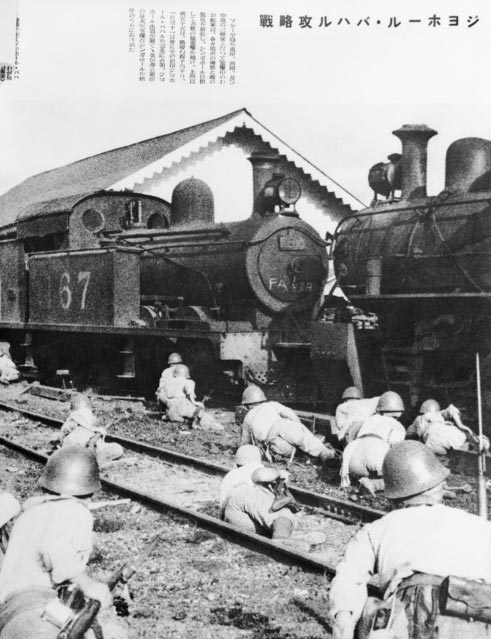
The RAAF and eight Australian warships fought the Japanese Army as it invaded Malaya on 8 December 1941. The highly experienced Japanese Army quickly took over the city of Kuala Lumpur and moved towards Singapore. The two battleships that Britain sent to defend Singapore’s naval base were sunk on 10 December 1941. The Japanese forces reached Singapore in only two months, after fighting the 700 kilometres from their landing point to the city.
Singapore was poorly defended, with no planes or ships left to protect it from Japanese bombing. The British Empire’s soldiers (including Australians) were spread too thinly to stop the Japanese Army from landing on the north-west of the island on 8 February 1942.
Research task
Do some research to find out why British Prime Minister Winston Churchill called the fall of Singapore ‘the worst disaster and greatest capitulation in British history’.

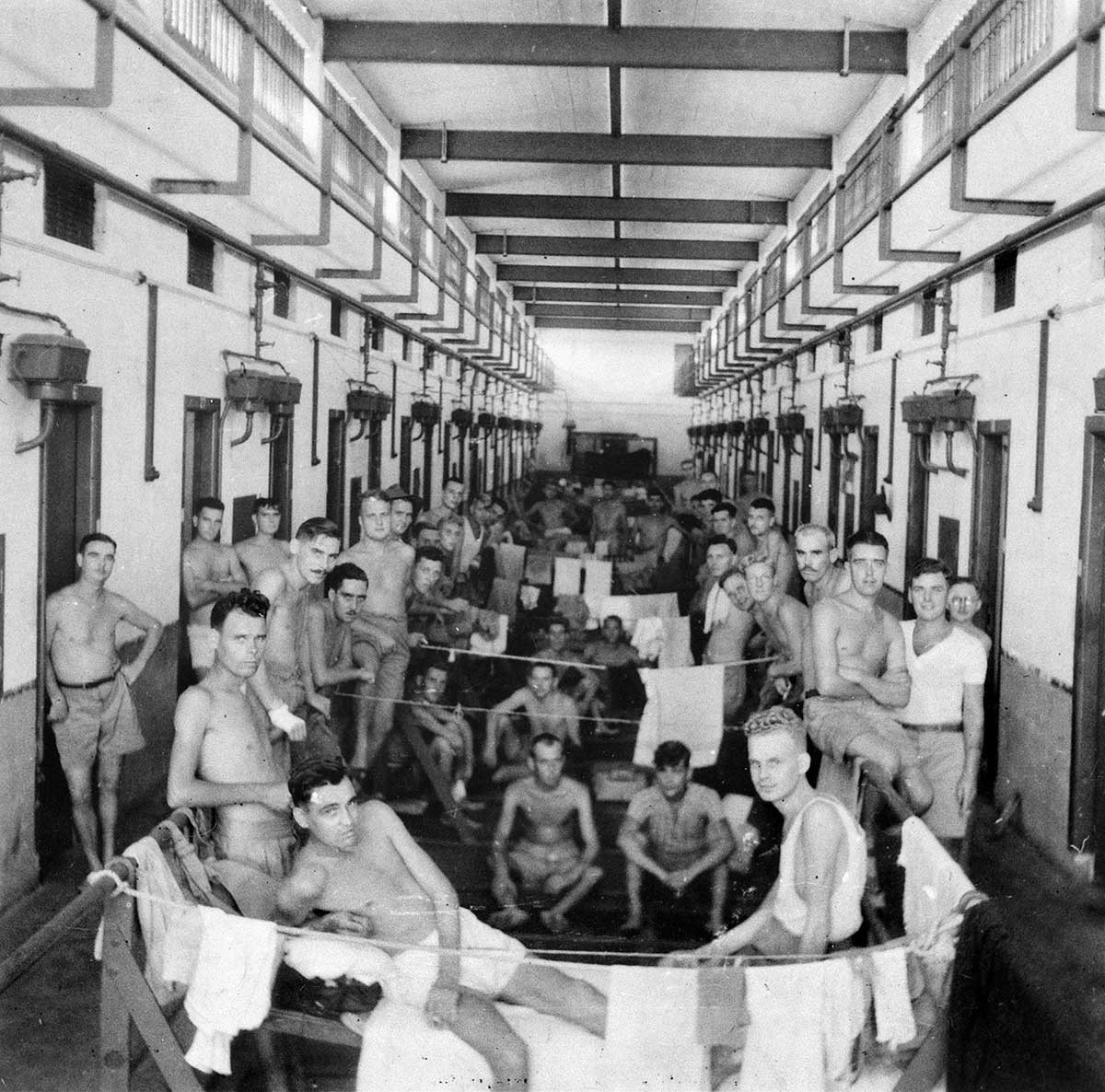
Only one week later, on 15 February 1942, the British commander Arthur Percival surrendered Singapore after the city nearly ran out of water. Major General Gordon Bennet, the commander of the Australian forces in Singapore, escaped the night before the surrender. More than 15,000 Australian soldiers were captured (almost a quarter of Australia’s overseas soldiers), and 7000 later died as prisoners of war.
What effect did the fall of Singapore have on Australia?
After Japan won a naval victory against Russia in 1905, Australian Prime Minister Alfred Deakin invited the United States Navy to visit Australia. This event, followed by the fall of Singapore and American victories in the Pacific, made Australia look to the United States as a powerful ally.
After the British Empire collapsed following the Second World War, Australia increasingly relied upon the United States for military support. Australia’s alliance with the United States continued throughout the Second World War (1939–45), the Korean War (1950–53) and the Vietnam War (1964–75), and remains in place today.
Read a longer version of this Defining Moment on the National Museum of Australia’s website.
Research task
How were Allied prisoners of war (including Australians) treated at Changi in Singapore? You will find some useful information on the Australian War Memorial website.
 What did you learn?
What did you learn?
1. Why did Australia and New Zealand build a naval base in Singapore?
2. How successful was the Japanese invasion of the Malay Peninsula? What contributed to this success?
3. What events led Australia to rely on the United States for its defence after the fall of Singapore?