Movement of peoples Defining Moments, 1750–1901

- Year level 9
- Investigations 3
- Activities 11
- Curriculum topic Movement of peoples
1. Overview of the learning module
Introduction
This learning module provides resources and classroom activities for teachers to use in their Australian Curriculum: Humanities and Social Sciences Year 9 classrooms.
It supports the History knowledge and understanding strand for Depth Study 1, Making a better world? Movement of peoples (1750–1901).
The learning module focuses on the four key inquiry questions in the Depth Study:
- What movements of people occurred?
- What were the migration experiences of people?
- How did migration change their lives?
- What impacts did migration have on the new homeland?
The learning module is self-contained, and can be used in any of the following ways:
- as whole class activities with all students studying a number of Defining Moments in Australian History that help them understand aspects of Australia’s history
- distributed between small groups, with students reporting back on their findings to the whole class
- as selected enrichment activities for individual students.
The investigations provide a rich digital resource for classroom use. They include contextual information, documents, images, scaffolded comprehension, analytical and extension questions, and individual, group and class activities. Using these materials and activities, students can explore aspects of twentieth century Australian history through text, images and objects.
The learning module has been designed to draw on the National Museum of Australia’s Defining Moments in Australian History, together with some supplementary resources.
What constitutes a defining moment in Australian history, and why some issues and situations can be considered more significant than others, is an underlying theme that can be raised with students throughout the module.
Module snapshot
The learning module can be used to create a set of preliminary ideas, understandings and questions that will help students investigate the topic in more detail.
It contains:
- Setting the scene
Get students to research, compare and discuss different definitions and understandings of key terms such as migration, Aboriginal, imperialism, industrialisation, nationalism (or national identity), empathy, primary source and source analysis.
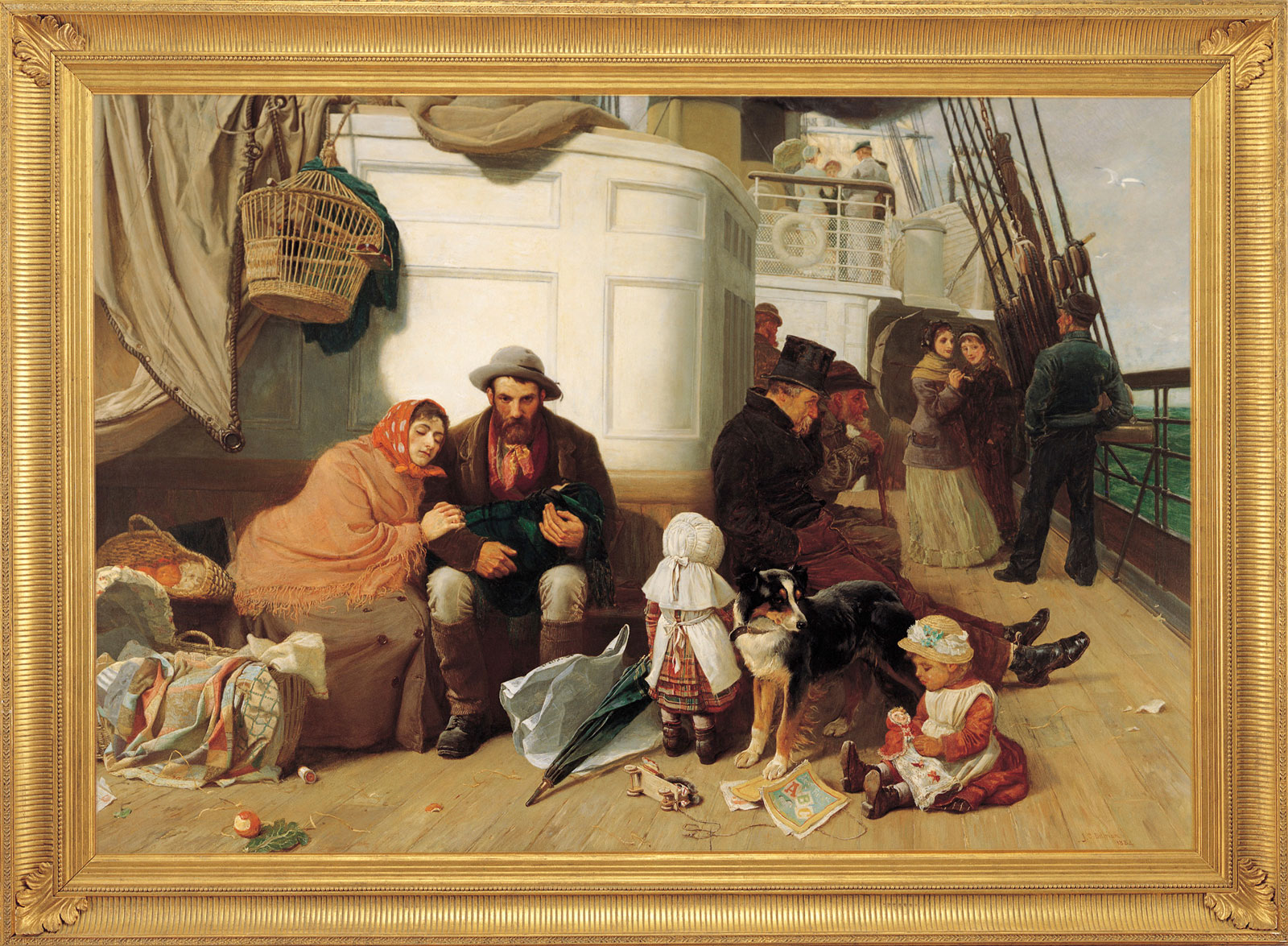
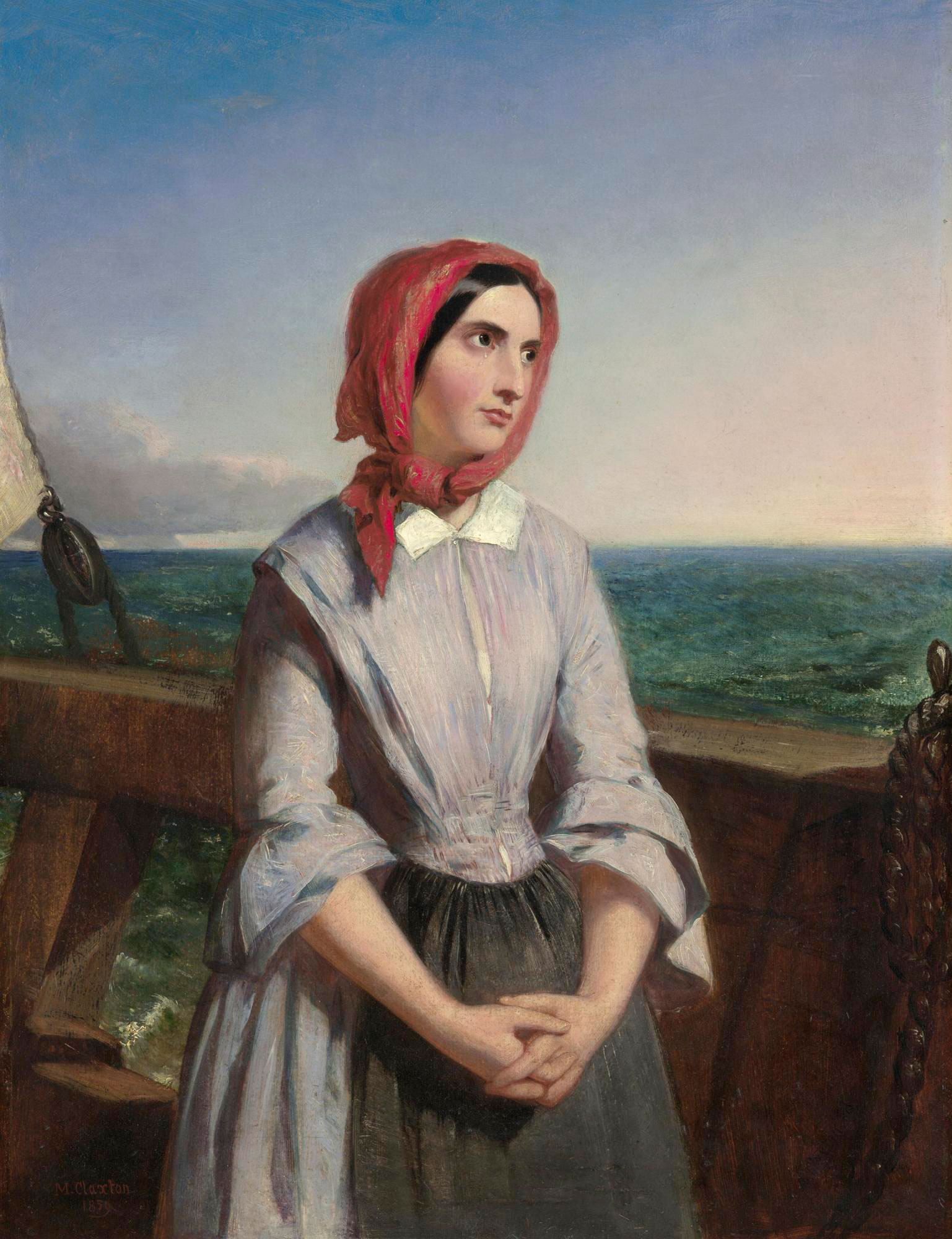
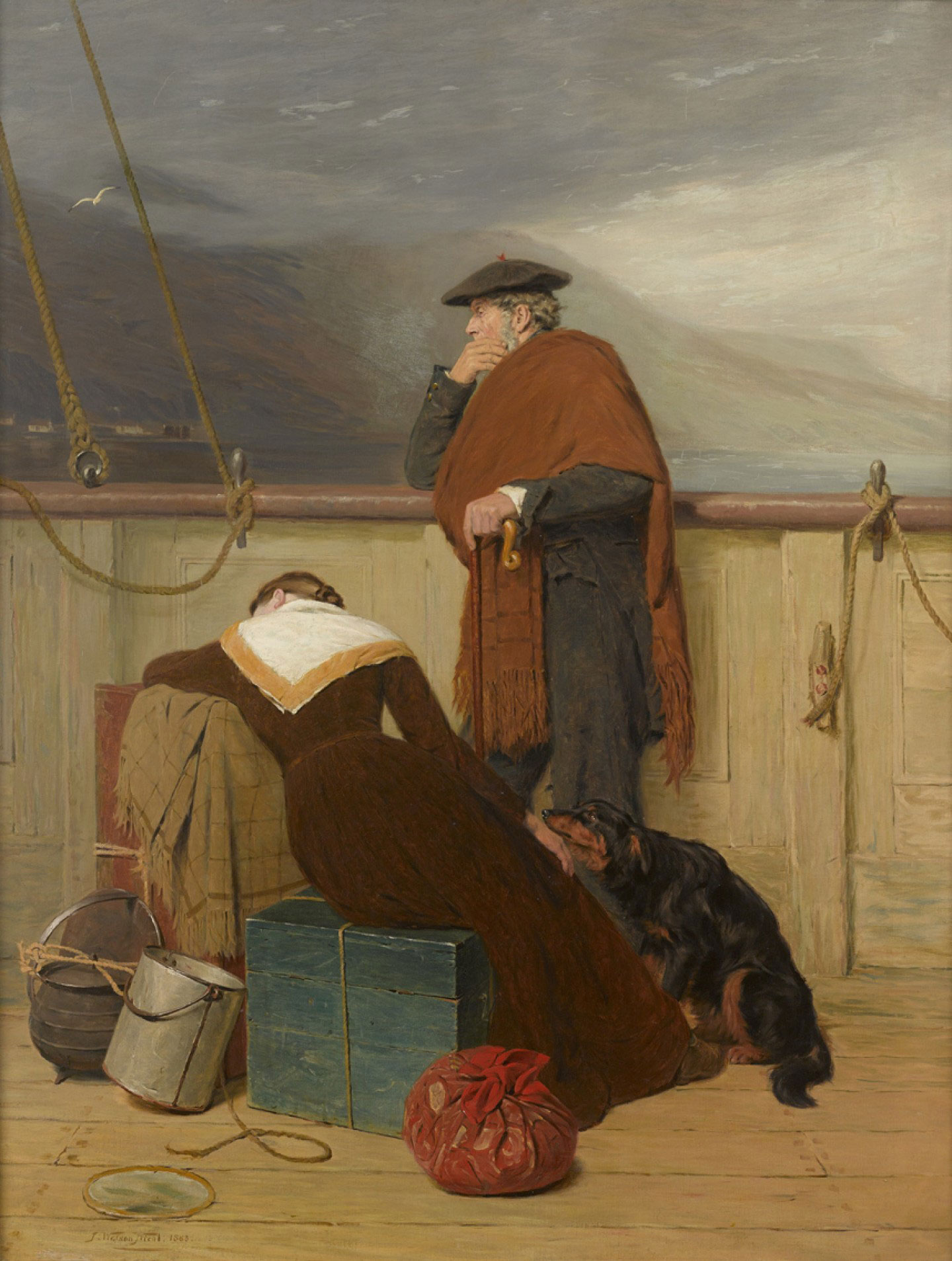
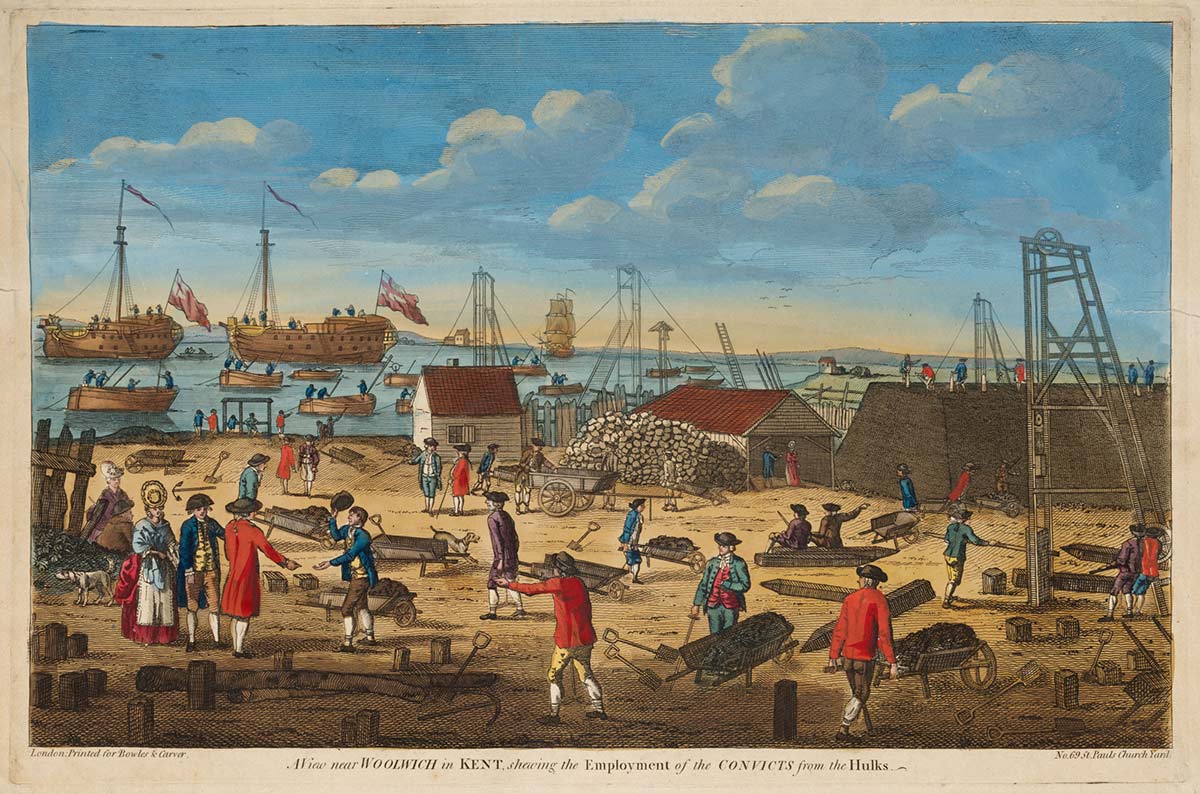
Introduce students to the key elements of the migration experience by having them consider what it means to be part of a migrant family. This can be helped by the set of stimulus images provided.
This imaginative and empathetic introduction can lead to students creating a set of key investigative questions that can guide them in their own subsequent learning about different groups.
- Investigations 1.1–1.5
Have students look at one or more of the five Defining Moments in the investigation. These, together with a set of investigative questions, provide a starting point for learning about migrant experiences in Australia.
- Investigation 2.1
This case study involves students exploring a greater variety of evidence in order to learn about one migrant group in more depth. Students can use this as a model for identifying the sorts of information and evidence that they may find in their own investigations.
- Investigation 3.1
This concluding investigation provides students with an example of the impact of migration on Australian attitudes and values as expressed by the Bulletin, which came into existence in the second half of the nineteenth century. Through further research students can then consider whether the attitudes expressed in the Bulletin towards Chinese migrants were representative of wider Australian attitudes and values towards Chinese migrants in particular, and migrants more generally.
- Bringing it together
This final section asks students to reflect on what they have learned about the Australian nineteenth century migrant experience.
2. Student activities
Student activities
Setting the scene
Investigation 1: Migration experience starting points
Investigation 2: Migration case study
Investigation 3: Attitudes towards migration case study
Bringing it together
3. Relevant Defining Moments in Australian History
The learning module draws on the resources on the Defining Moments in Australian History website, together with supplementary materials.
Defining Moments that are relevant to the inquiry questions in the curriculum include:
| Year | Defining Moment | Investigation |
|---|---|---|
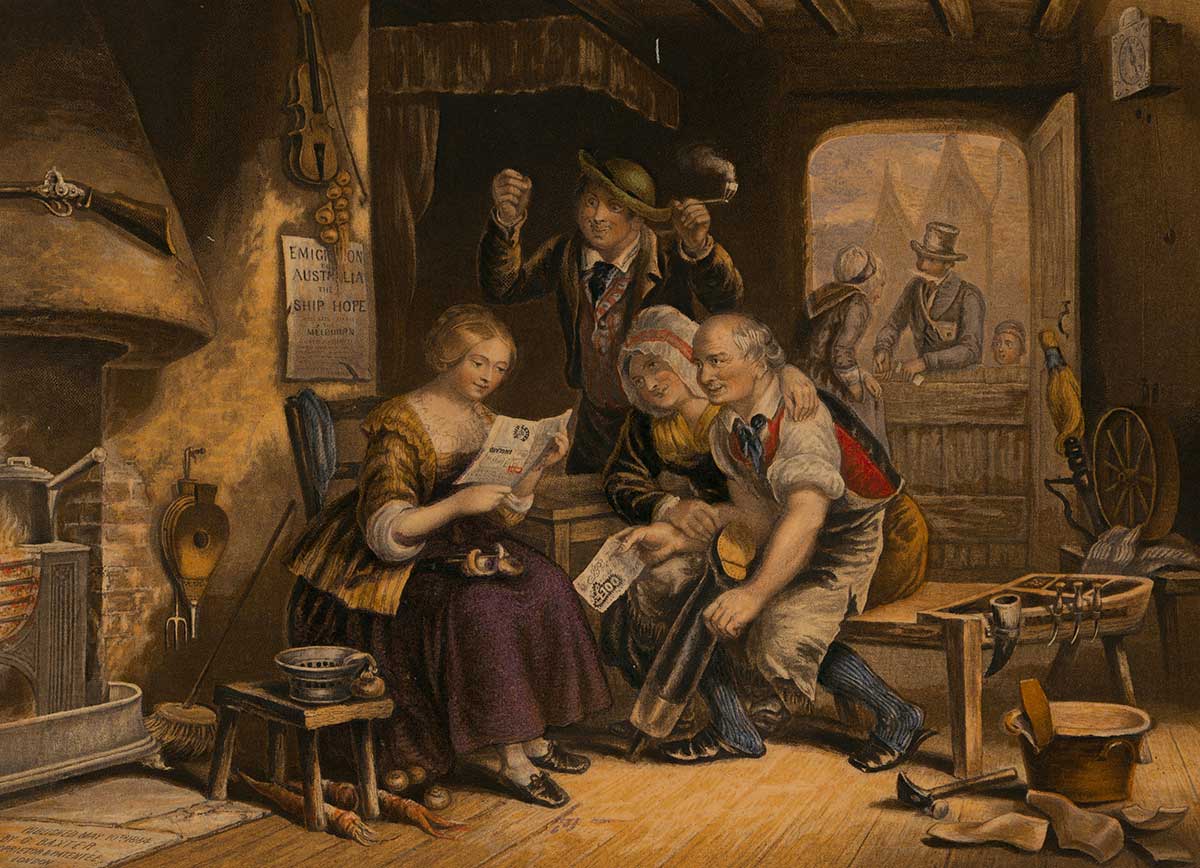
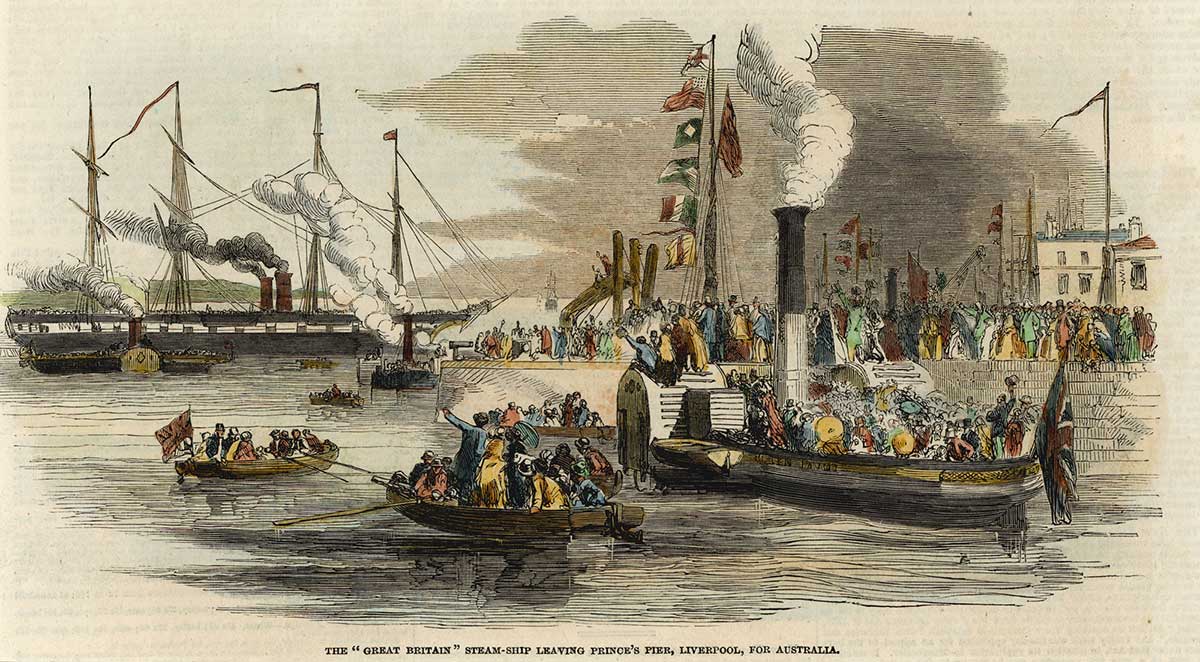
| 1832 | Introduction of assisted migration | Investigation 1 |
| 1833 | Convict transportation to Australia peaks when nearly 7000 people arrive in one year | Investigation 1 |
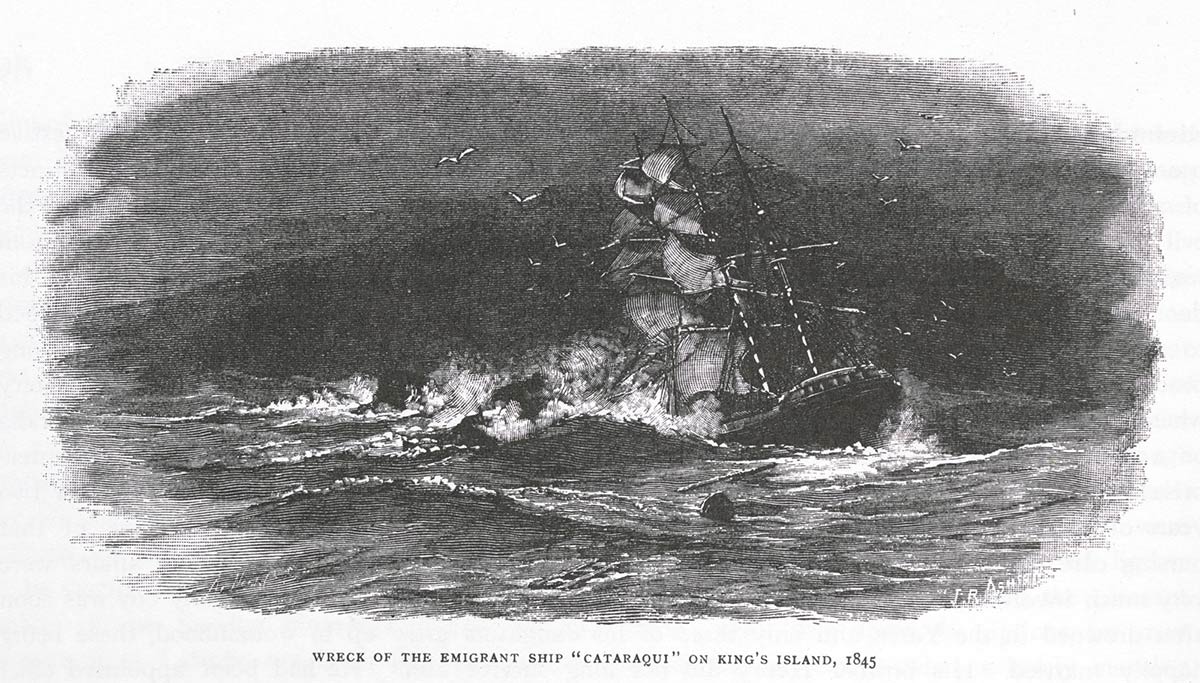
| 1845 | Cataraqui wrecks off King Island — 400 die in Australia’s deadliest maritime civil disaster | Investigation 1 |
| 1851 | Gold rushes in New South Wales and Victoria begin | Investigation 1 |
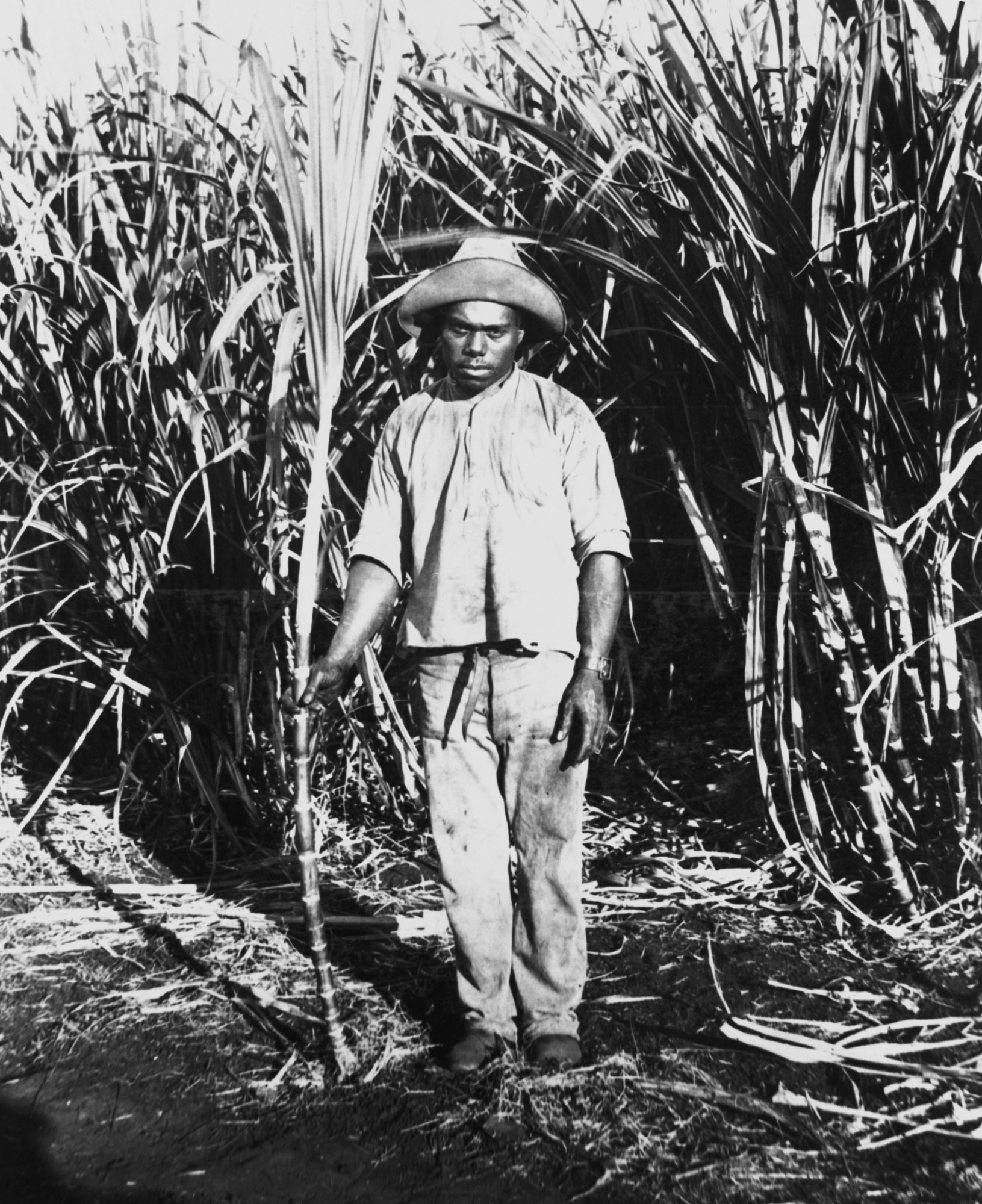
| 1863 | South Sea Islanders brought to Queensland as indentured labourers | Investigation 1 |
| 1880 | The Bulletin established | Investigation 3 |
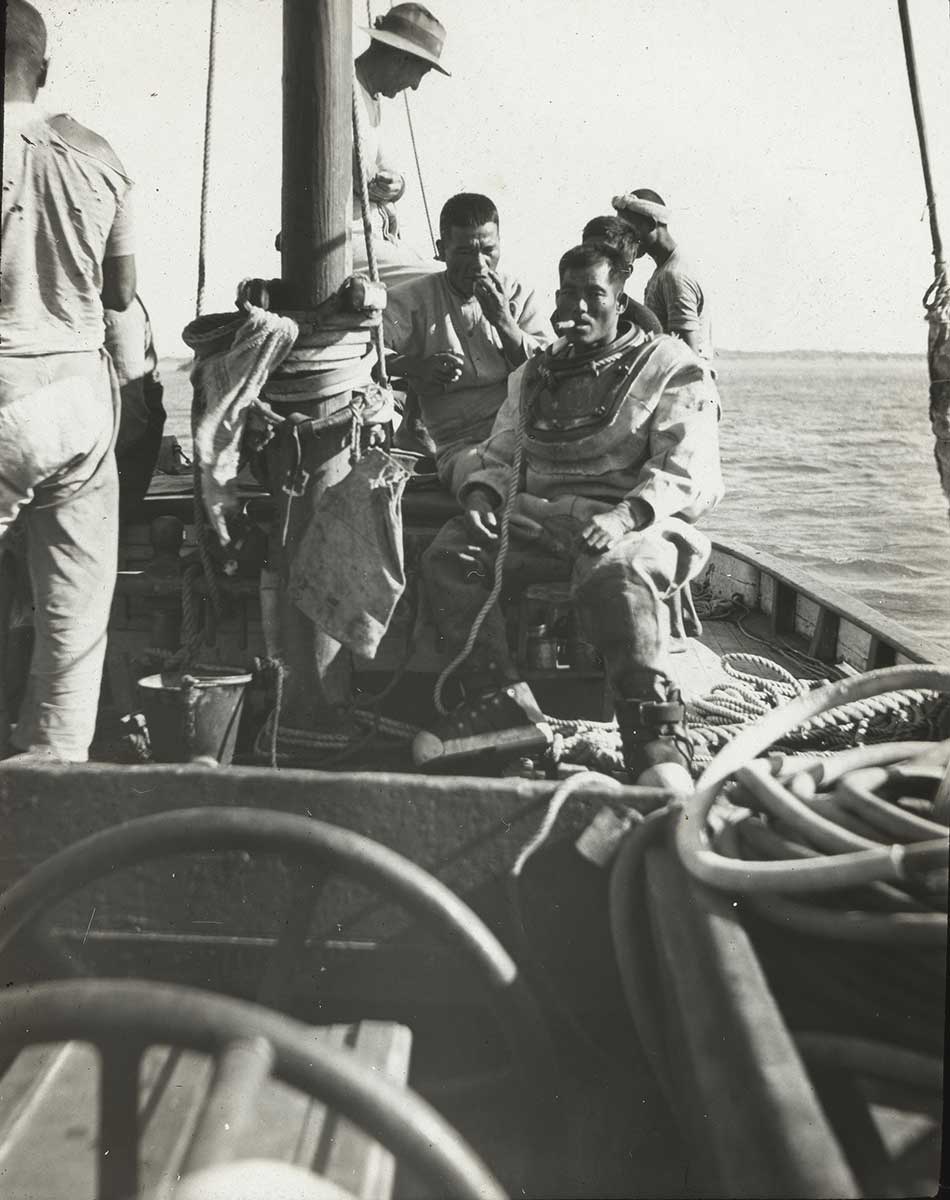
| 1888–89 | Japanese divers in Broome | Investigation 2 |
Simplified versions of the relevant Defining Moments are also available:
| Year | Defining Moment | Investigation |
|---|---|---|
| 1832 | ‘We can have a free passage’ — Assisted migration introduced | Investigation 1 |
| 1833 | A prison continent — Convict transportation peaks | Investigation 1 |
| 1851 | ‘A thousand cradles at work’ — Gold rushes begin | Investigation 1 |
| 1863 | ‘It was a form of slavery’ — First indentured Islander labourers | Investigation 1 |
| 1880 | ‘A journal which cannot be beaten’ — The Bulletin established | Investigation 3 |
| 1888–89 | Dangerous diving — Japanese divers begin pearling in Broome | Investigation 2 |
4. Australian Curriculum level and focus
Historical knowledge and understanding
Students will cover the following areas:
- The influence of the Industrial Revolution on the movement of peoples throughout the world, including the transatlantic slave trade and convict transportation (ACDSEH018)
- Experiences of slaves, convicts and free settlers upon departure, their journey abroad, and their reactions on arrival, including the Australian experience (ACDSEH083)
- Changes in the way of life of a group(s) of people who moved to Australia in this period, such as free settlers on the frontier in Australia (ACDSEH084)
- The short and long-term impacts of the movement of peoples during this period (ACDSEH085)
Historical skills
Students will exercise the following historical skills:
Chronology, terms and concepts
- Use chronological sequencing to demonstrate the relationship between events and developments in different periods and places (ACHHS182)
- Use historical terms and concepts (ACHHS183)
Historical questions and research
- Identify and select different kinds of questions about the past to inform historical inquiry (ACHHS184)
- Evaluate and enhance these questions (ACHHS185)
- Identify and locate relevant sources, using ICT and other methods (ACHHS186)
Analysis and use of sources
- Identify the origin, purpose and context of primary and secondary sources (ACHHS187)
- Process and synthesise information from a range of sources for use as evidence in an historical argument (ACHHS188)
- Evaluate the reliability and usefulness of primary and secondary sources (ACHHS189)
Perspectives and interpretations
- Identify and analyse the perspectives of people from the past (ACHHS190)
- Identify and analyse different historical interpretations (including their own) (ACHHS191)
Explanation and communication
- Develop texts, particularly descriptions and discussions that use evidence from a range of sources that are referenced (ACHHS192)
- Select and use a range of communication forms (oral, graphic, written) and digital technologies (ACHHS193)
Interdisciplinary thinking
Students will have engaged with the concepts of:
- significance
- continuity and change
- cause and effect
- place and space
- interconnections
- roles, rights and responsibilities
- perspectives and action.
Cross-curriculum priorities
Students will have been involved in additional learning about aspects of:
- Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander societies
- Asia and the Pacific
- sustainability.
Source: The Australian Curriculum Humanities and Social Sciences v8.3, December 2016, viewed 1 November 2018
5. History outcomes matrix
All case studies in the learning module have been designed to help students develop the knowledge and skills outcomes specified in the Australian Curriculum — History. At the end of each case study teachers could use this matrix to help guide student discussion about what they have achieved from the case study. The matrix is suitable to be used from Years 5–10, but with teachers guiding the discussion as appropriate to the particular class. It could also be used for assessment purposes.
| Outcome | Elaboration or explanation | Applying this to each case study |
|---|---|---|
| KNOWLEDGE | Comprehending what happened factually. | What happened? |
| UNDERSTANDING | Being able to explain what happened and why. | Explain why it happened. |
| CHRONOLOGY | Knowing how events occurred in time and place. | Explain how events unfolded. |
| CAUSE AND EFFECT | Understanding why events occurred as they did and the impacts or effects they had. | Explain the causes of the event and its impacts. |
| EMPATHY | Looking at events from the different perspective of participants. | Why do you think people at the time might have behaved in this way? |
| CHANGE AND CONTINUITY | What changed and what remained the same after the event. | Explain how the event changed some aspects, but not others. |
| VOICE OR AGENCY | Understanding whose voice or perspective is included and excluded in the record of the event. | Which people or groups involved in, or affected by, the event have been represented? Which groups have not yet been represented? |
| JUDGEMENT | Deciding on the benefit or harm created by the event. | Explain why you think the event was beneficial or harmful, or both. |
| SIGNIFICANCE | Explaining why it might be considered a ‘Defining Moment’ in Australian history. | Do you think it was a significant and impactful event? Explain why you do or do not think this event is significant to Australian history. |
6. History source analysis guide
Some of the case studies involve students using historical skills to evaluate primary sources of evidence. This process involves identifying ‘bias’ but also many other features of the evidence. Students can use a source analysis guide to help them interrogate sources.
| Aspects | Elaborations | Document | Image | Artefact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DESCRIPTION | How would you describe or classify it? What type of evidence is it? | e.g. an official government report, a diary entry, transcript of an interview recorded 40 years after the event | e.g. a photograph from the time, a propaganda poster, a satirical cartoon | e.g. a made object |
| ORIGIN | Who created it? When? Where? | e.g. an eyewitness account from a participant on one side, a family story handed down for generations, a newspaper report that quotes several participants | e.g. an eyewitness, a government body, a newspaper cartoonist | e.g. created at the time, used at the time, technique used, materials used, made by all or specialised skills |
| CONTEXT | What were the conditions at the time? How could they have influenced its creation? | e.g. created during a period of crisis, created years later after the events had finished | e.g. created during a period of crisis, created years later after the events had finished | e.g. typical of the time or an innovation, specialised or mass production |
| AUDIENCE | Who was it created for? How widespread would it have been? | e.g. a political party, a mass protest, an official inquiry, a personal record | e.g. a political party, a mass protest, an official inquiry, a personal record, a readership | e.g. elite people or ordinary people |
| PURPOSE | Why was it created? What is its style or tone? | e.g. as an official record, to influence people to join a political party, to criticise somebody | e.g. to entertain, to persuade or influence, to criticise, to reveal information, to record facts | e.g. everyday use or specialised use, domestic use or trade |
| RELEVANCE | What does it help you know and understand about what you are investigating? | e.g. people involved, places, times, attitudes, values of the time, supporters and opponents | e.g. people involved, places, times, attitudes, values of the time, supporters and opponents | e.g. work, leisure, education, attitudes, values, everyday life, food |
| RELIABILITY | What is its authority, accuracy and believability? | e.g. factual accuracy, person in a position to know, first-hand or second-hand | e.g. factual accuracy, person in a position to know, first-hand or second-hand | e.g. typical or unusual, how closely associated with the events |
7. Learning at the National Museum of Australia
Enjoying our online teaching resources? Why not check out what else we have to offer?
We run onsite school programs, digital excursions and teacher professional learning programs.
Discover more about defining moments in Australian history through these curriculum-linked learning activities.











![Deep Sinking , Bakery Hill, Ballaarat [sic] 1853', by Samuel Thomas Gill](/sites/default/files/2020-07/Yr9_MovementPeoples_9.jpg?v=1?v=1)



