Learning module:
Second World War Defining Moments, 1939–1945
Investigation 2: The Australian military experience of the war
2.5 Did the men of Kokoda help save Australia from invasion?

In 2008 the Australian Government declared that the first Wednesday of September each year was to be the official day of commemoration for the Battle for Australia. ‘Battle for Australia Day’ was to recognise ‘the service and sacrifice of all those who served in defence of Australia in 1942 and 1943’.
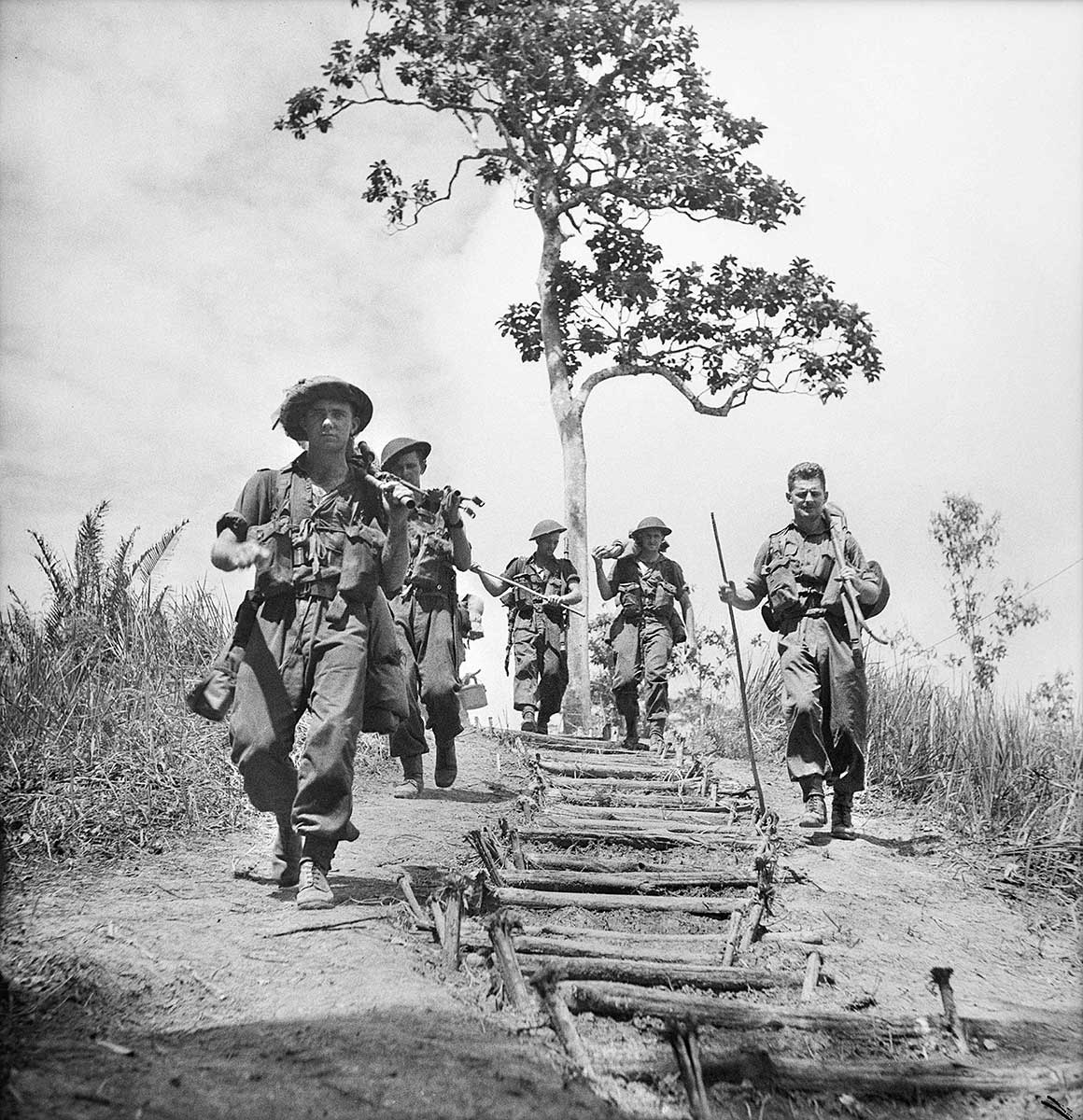
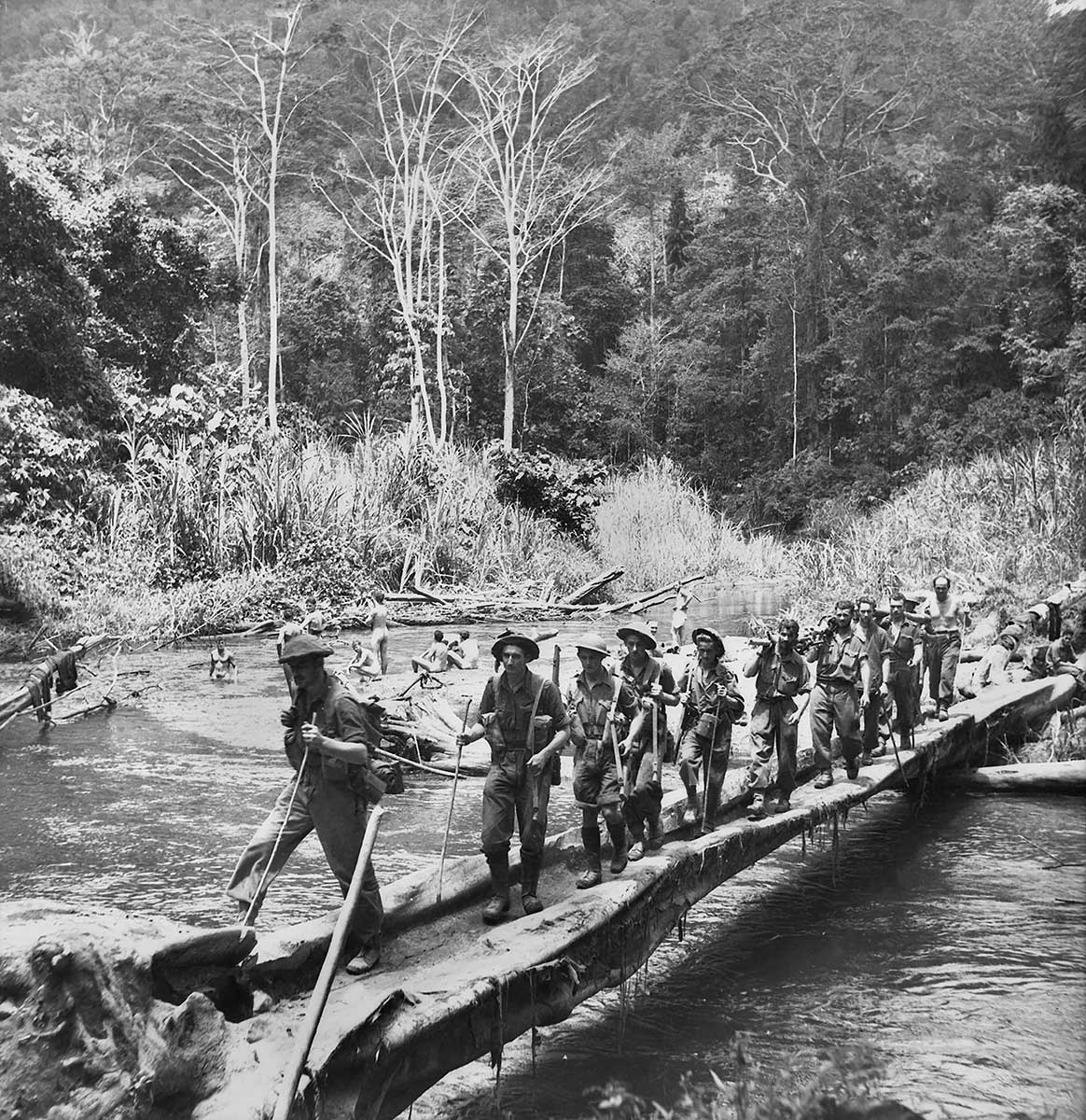
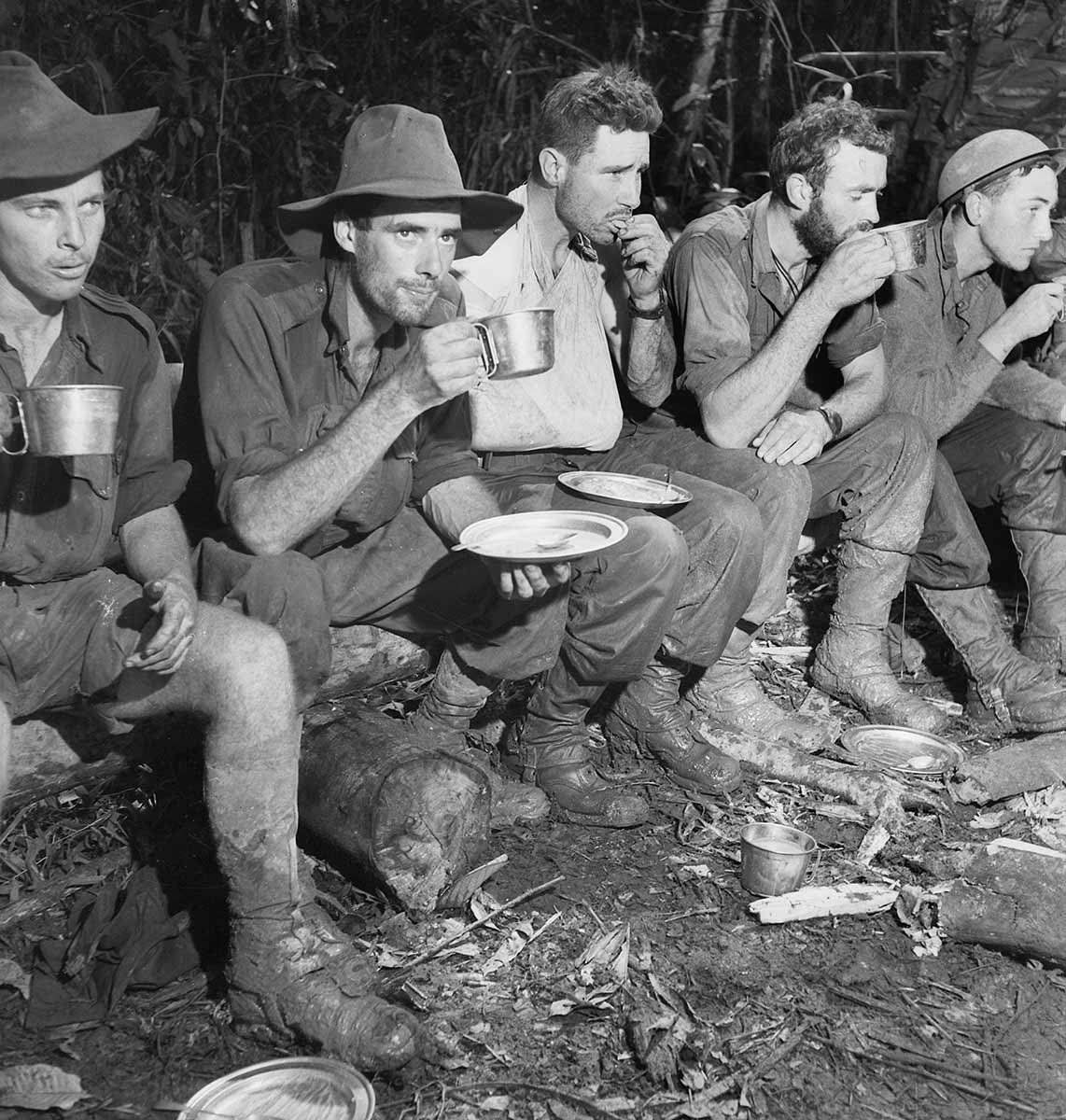
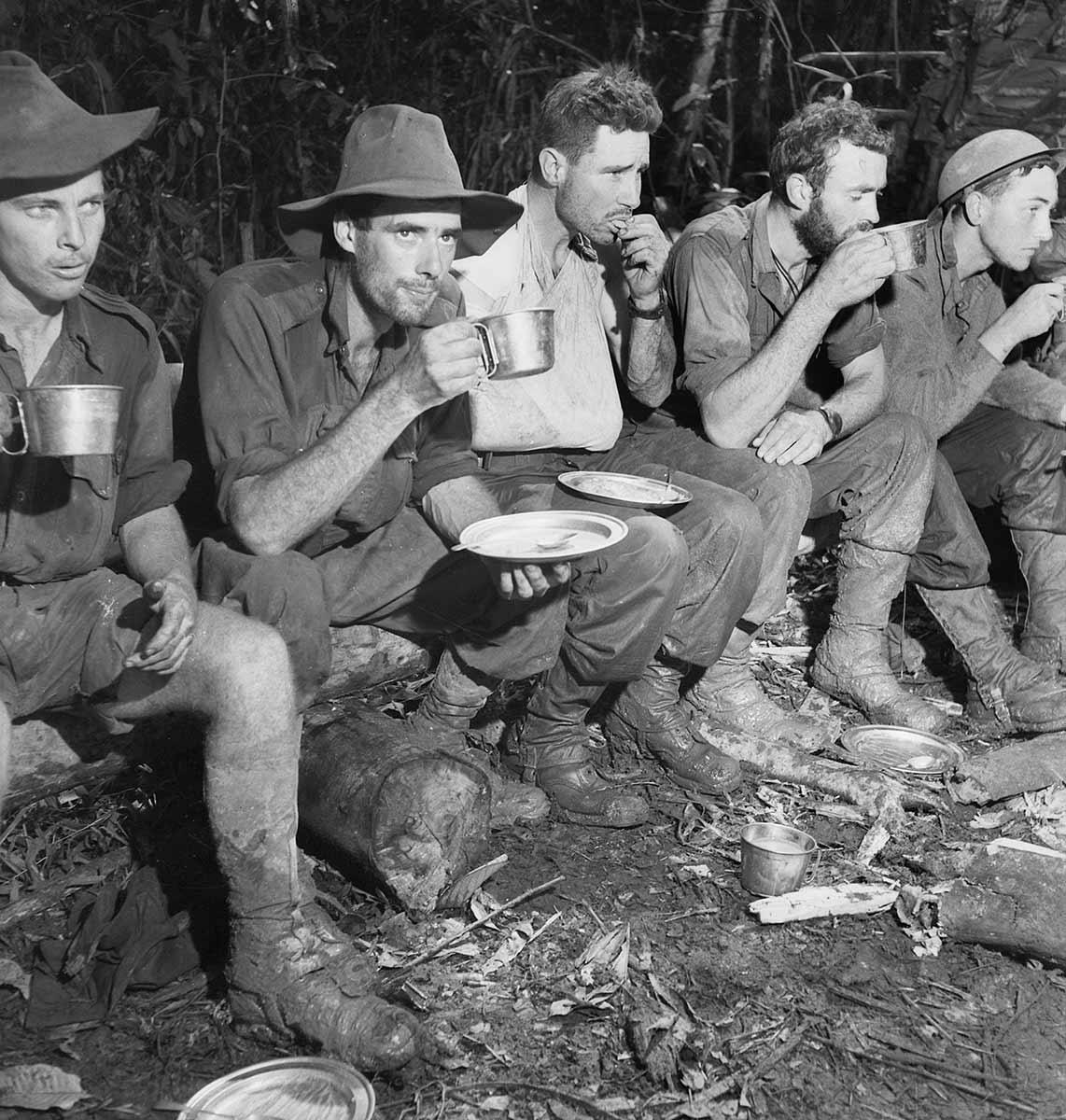
The Battle for Australia included the Battle of the Kokoda Trail, the Battle of Milne Bay, the Battle of the Coral Sea, and the Battles for Buna, Gona and Sanananda.
Some people claim that Australia was in danger of Japanese invasion in 1942, and the Battle for Australia stopped that.
Others argue that there were never any plans to invade Australia, so there was never any real danger of invasion. They do not deny or minimise the sacrifice of those involved in fighting, nor that it helped defeat the Japanese, but they say that it did not stop any invasion because none was planned.
Your task is to consider this controversy. You will be able to come to your own conclusion by using the evidence below. You will also find ideas and language that are unacceptable today. There are five questions to consider in coming to your conclusion.
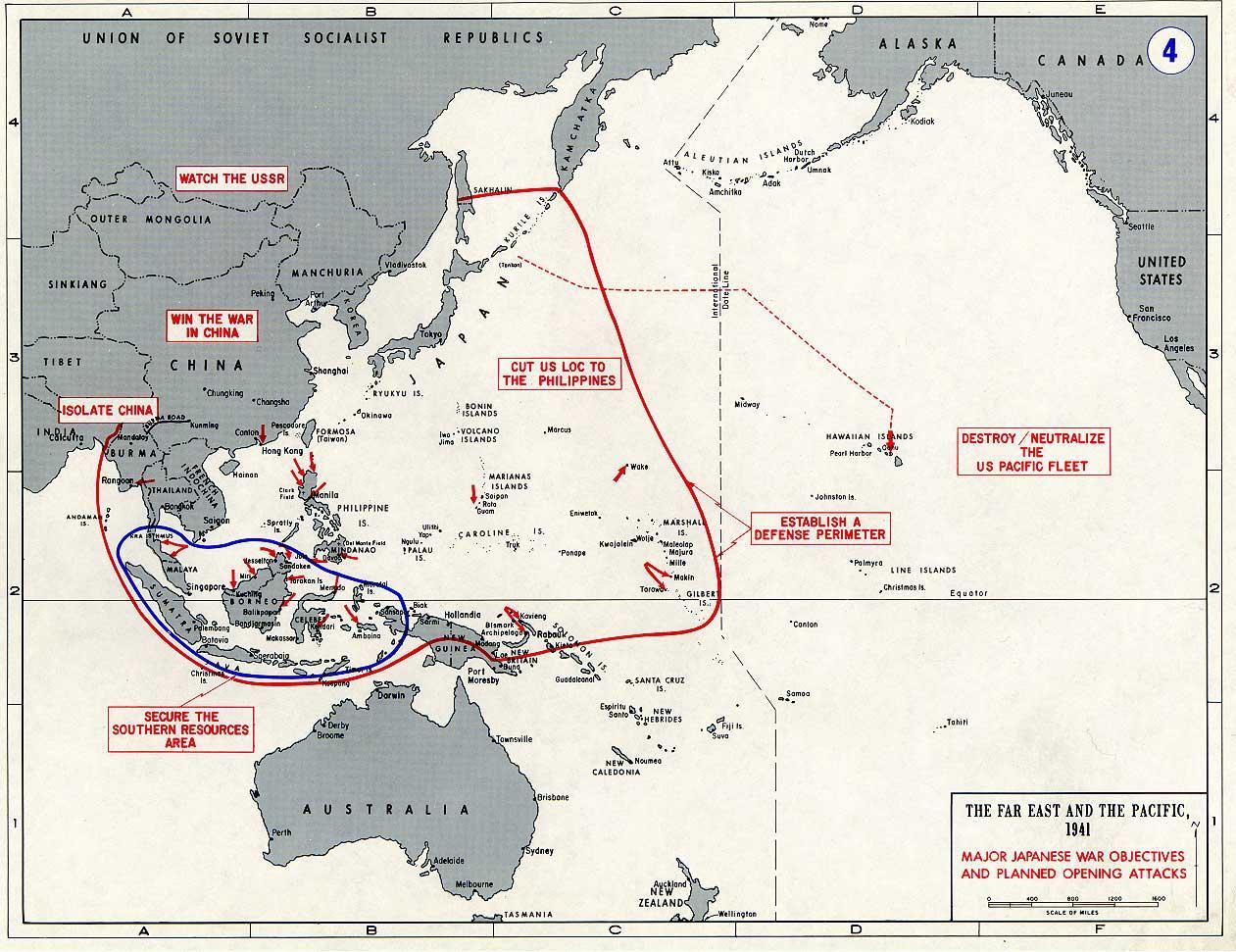
1. Start by looking at the Background information, a summary of events in 1942, showing the seriousness and closeness of the Second World War for Australia.
Background information: 1942 a year of threat
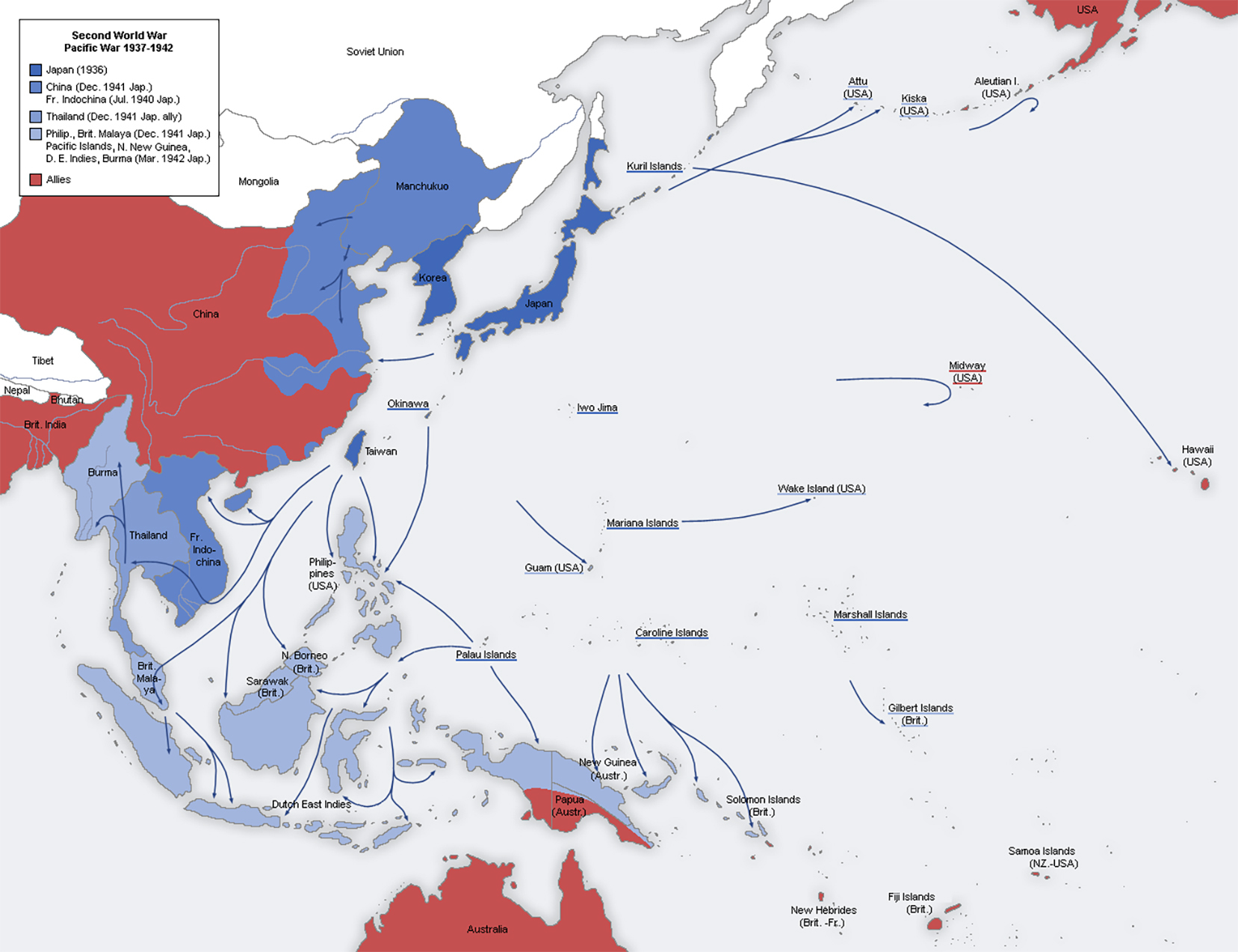
Significant events in the Pacific War December 1941 – January 1943
|
1941 |
|||
|
7–8 December |
Japan invades Thailand and Malaya, and attack the US naval base at Pearl Harbor, Hawaii. |
||
|
26 December |
Fall of the British colony of Hong Kong. |
||
|
1942 |
|||
|
23 January 31 January |
Rabaul surrenders, 1,400 Australian troops killed or captured. British and Australian troops in Malaya forced on to Singapore Island. |
||
|
2 February 15 February 19 February 20 February 27 February |
3,600 Australian and Netherlands East Indies troops killed or captured at Ambon. Surrender of Singapore — 140,000 Dominion troops, including nearly 17,000 Australian troops, killed or captured. First of 64 air raids on Darwin kills at least 243 people. 2,400 Dutch, Portuguese and Australian troops killed or captured in Timor. HMAS Perth sunk, 686 crew died of taken prisoner. |
||
|
3 March 8 March 22 March |
Air raids on Wyndham, Broome. Japanese troops take Lae, Salamaua; Air raid on Derby. Air raid on Katherine. |
||
|
4–8 May 6 May |
Japanese invasion fleet for Port Moresby stopped at Battle of the Coral Sea. Fall of the Philippines. |
||
|
1 June 4–6 June 8 June |
Midget submarine attack on Sydney Harbour killing 19 sailors. Japanese and US fleets suffer great losses at Battle of Midway. Newcastle shelled by a Japanese submarine. |
||
|
22 July 26–29 July 28 July |
Japanese start along Kokoda Trail to capture Port Moresby. Three Japanese bombing raids on Townsville. Japanese force takes Kokoda. |
||
|
7 August 8 August 9 August 25 August 27 August |
US landing at Guadalcanal puts great pressure on Japan to withdraw troops from Kokoda Trail. Australians re-take Kokoda. HMAS Canberra sunk killing 80 crew. Start of Japanese invasion of Milne Bay, which was defeated by Australian and American troops. Japanese re-take Kokoda, Australians start a fighting retreat. |
||
|
17 September 24 September |
Japanese reach Imita Ridge, 40km from Port Moresby. Japanese troops ordered to withdraw from Ioribaiwa, to provide reinforcement troops for Guadalcanal. |
||
|
1–31 October |
Fighting along the Kokoda Trail. |
||
|
11 November |
Defeat of Japanese at Oivi-Gorari ends the Battle of the Kokoda Trail. |
||
|
2 December 9 December |
Australians and Americans defeat Japanese at Buna. Australians and Americans defeat Japanese at Gona. |
||
|
1943 |
|||
|
18 January |
Australians and Americans defeat Japanese at Sanananda. |
||
|
1 February |
Australian troops defeat Japanese at Wau. From this point on Japan is gradually defeated in all areas of the Pacific. |
||
2. Look at the sources below. For each, decide which of the Five key questions it helps you to answer. When you have finished considering all the evidence, you will be able to decide whether or not you think Australia was in danger of invasion by Japan during the Second World War.
Five key questions
|
A Did people fear invasion? |
B Did the Government fear invasion? |
C Did the Japanese have an invasion plan? |
D Did the Japanese have the ability to invade? |
E Did Kokoda, as part of the Battle for Australia, save Australia from invasion? |
3. Now that you have considered all the evidence and the five key questions for each one, answer these concluding questions and give reasons for your answers.
a) Do you think Australians feared an invasion in 1942? If so, was that fear justified?
b) Do you think the Government feared an invasion? If so, was that justified?
c) Do these sources suggest that Japan planned to invade Australia?
d) Do these sources suggest that Japan was capable of invading Australia?
e) Do you think the Battle for Australia save Australia from invasion? Does the answer to this question affect your opinion as to whether or not you think we should commemorate the Battle for Australia?